- Healthcare 150
- Posts
- The Rise of Robotic Surgery and the Emerging Role of AI in the Operating Room
The Rise of Robotic Surgery and the Emerging Role of AI in the Operating Room
Surgical innovation has entered a new era with robotic-assisted surgery rapidly gaining traction across specialties, as highlighted by Bain & Company and HCA’s leading role in robotic operations.

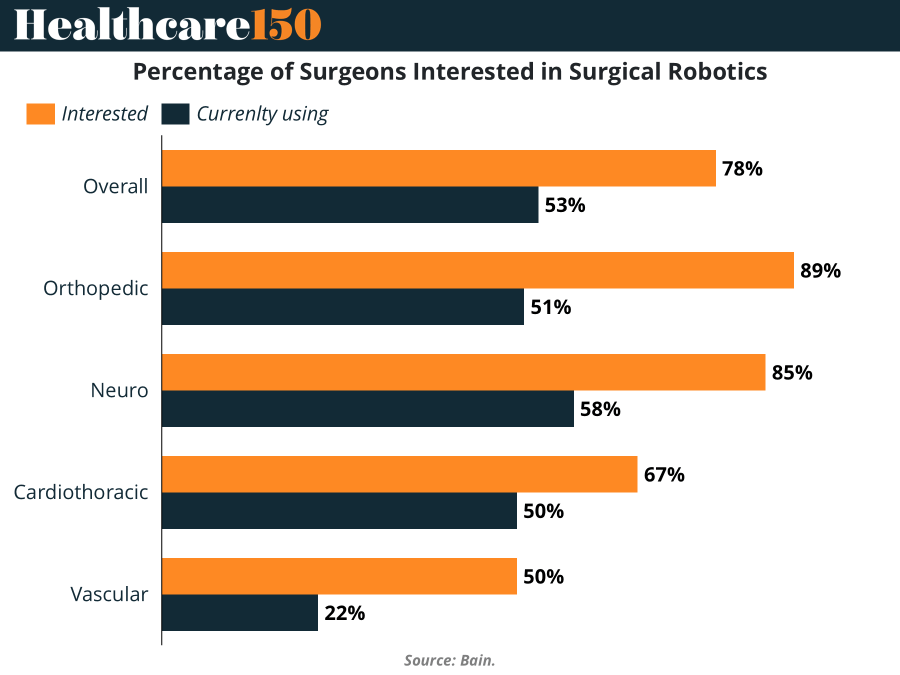
The chart accompanying Bain’s recent report reveals a growing interest in surgical robotics among physicians: 78% of surgeons overall are interested, though only 53% are currently using the technology. This gap between interest and adoption reflects a broader story of how innovation diffuses through healthcare — a tale now repeating itself with artificial intelligence (AI).
Orthopedic and neurosurgeons show the highest interest in robotics (89% and 85% respectively), but actual usage remains significantly lower (51% and 58%). Cardiothoracic and vascular surgeons lag further behind, with only 50% using robotic tools despite growing curiosity. This discrepancy suggests that while excitement around robotic capabilities is high, integration into surgical workflows still faces structural, financial, and training barriers.
Yet, the robotic surgery market is maturing quickly. As HCA’s medical director of robotics described, their health system has performed over a million robotic-assisted surgeries and sees the technology not as a surgeon replacement but as a tool to enhance outcomes, efficiency, and surgeon capabilities. This mindset has driven adoption — not through the threat of obsolescence but through empowerment and tangible return on investment (ROI).
That insight offers a useful lens to examine AI in clinical practice, particularly in the burgeoning AI scribe market. According to the Peterson Health Technology Institute (PHTI), AI scribe adoption is accelerating, with some health systems seeing 70%–80% uptake when implemented departmentally. However, much like robotics, enthusiasm is tempered by real-world considerations: inconsistent usage rates, ROI concerns, and varied implementation strategies.
Bill Gates recently predicted that AI could render physicians largely unnecessary within a decade. While the technology may soon reach such potential, the robotic surgery market tells us that clinical disruption doesn’t hinge solely on capability. It depends on organizational buy-in, workflow integration, and ROI. The adoption curve of robotic surgery — led by companies like Intuitive Surgical, whose success hinged on surgeon-centered marketing and administrative alignment — suggests that AI must follow a similar path: supporting clinicians, not replacing them.
Interestingly, AI scribes are beginning to evolve beyond mere documentation assistants. With vendors eyeing adjacent use cases like revenue cycle management (RCM), the push for broader utility mirrors how robotic platforms expanded their surgical applications. This convergence hints at a future where surgical robots and AI tools are increasingly intertwined — with AI powering robotic platforms through enhanced visualization, decision support, and real-time analytics.
In short, while surgical robots have established a foothold by proving ROI and enhancing surgical performance, AI now faces a similar challenge: converting interest into sustainable adoption. The data suggests the key lies not in replacing clinicians, but in amplifying their impact. Robotic surgery's journey offers both a roadmap and a cautionary tale for AI’s role in the operating room and beyond.
Sources & References
Bain. (2025). Navigating the Next Wave of Surgical Robotics. https://www.bain.com/insights/navigating-the-next-wave-of-surgical-robotics/
Health Tech Nerds. (2025). PHTI on AI scribe adoption, robotic surgery and AI, 23andMe files for bankruptcy, and more. https://www.healthtechnerds.com/p/weekly-health-tech-reads-3-30-25
Peterson Health Technology Institute. (2025). Adoption of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Delivery Systems: Early Applications and Impacts. https://phti.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2025/03/PHTI-Adoption-of-AI-in-Healthcare-Delivery-Systems-Early-Applications-Impacts.pdf