- Healthcare 150
- Posts
- The Global Obesity Therapeutics Market: Transforming a Major Health Challenge into a Pharmaceutical Megatrend
The Global Obesity Therapeutics Market: Transforming a Major Health Challenge into a Pharmaceutical Megatrend
The global market for obesity therapeutics has entered a period of explosive transformation, reshaping both healthcare and the pharmaceutical industry.

Introduction
Once considered a niche therapeutic area, obesity treatment has now become a strategic frontier for innovation, investment, and healthcare reform.
Fueled by scientific breakthroughs—most notably the success of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists such as semaglutide and tirzepatide—the obesity therapeutics market is now one of the fastest-growing sectors globally. According to McKinsey, the market could reach between $120 billion and $280 billion by 2040, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9–15% from 2022 levels.
This surge reflects not only the medical potential of new anti-obesity drugs but also the growing recognition of obesity as a chronic, treatable disease with systemic implications for public health, healthcare expenditure, and the global economy. Historically, obesity was stigmatized and under-treated, often perceived as a result of poor lifestyle choices rather than as a complex metabolic condition. Today, however, the scientific community acknowledges its multifactorial nature—driven by genetics, environment, behavior, and neuroendocrine regulation—which has opened the door to targeted pharmacological solutions.
The rapid evolution of obesity therapeutics coincides with a broader global health crisis. The World Health Organization estimates that more than 1.9 billion adults are overweight, and 650 million are obese, placing immense strain on healthcare systems. Beyond its individual health impact, obesity is now associated with over 200 chronic diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Alzheimer’s, and is projected to cost the global economy nearly $4 trillion annually by 2035.
Against this backdrop, pharmaceutical innovation has become not merely an opportunity but a necessity. Breakthrough therapies such as GLP-1 and GIP agonists have demonstrated profound clinical efficacy, transforming obesity from a largely intractable condition into a manageable chronic disease. As a result, the therapeutic category is evolving from a fringe specialty into a cornerstone of modern medicine—comparable in strategic significance to oncology and diabetes.
This report explores the multifaceted transformation of the global obesity therapeutics market, examining its growth trajectory, investment trends, evolving treatment modalities, and the emerging interplay between innovation, access, and policy. Together, these dynamics mark the beginning of a new era in which obesity management will shape not only the future of pharmaceuticals but also the health and economic well-being of societies worldwide.
Market Overview and Size
Global Market Growth
The obesity drugs market was valued at $20.20 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $86.71 billion by 2030, growing at a robust 27.5% CAGR. This trajectory places obesity therapeutics among the most dynamic growth areas in global pharmaceuticals, on par with oncology and diabetes treatments.
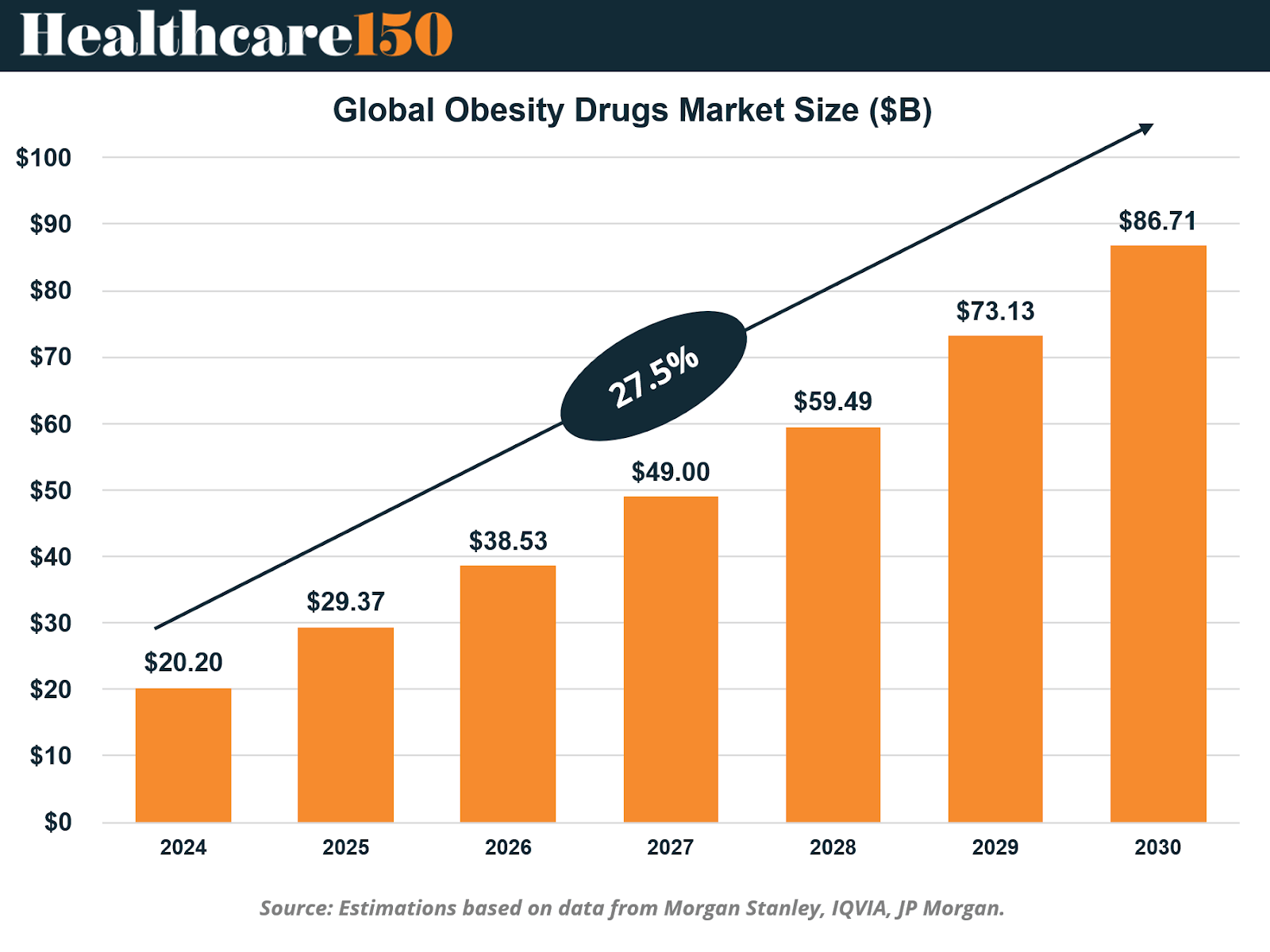
The adoption of GLP-1 and dual-agonist therapies has not only driven demand but also set a new clinical standard for efficacy, with average patient weight loss of 10–15%, according to IQVIA. These results have positioned obesity drugs as cornerstone treatments for both metabolic and cardiovascular health, marking a new phase of market maturity.
U.S. Market Dynamics
The United States remains the dominant force in the obesity therapeutics market, accounting for approximately half of global revenue. The U.S. market was valued at $9.5 billion in 2024 and is expected to expand to $47.53 billion by 2030, reflecting a 30.8% CAGR.
This impressive growth is being driven by multiple converging factors: the country’s high obesity prevalence, its advanced healthcare infrastructure, and its rapid adoption of novel GLP-1-based therapies. The U.S. market also reflects an evolving societal understanding of obesity—not as a lifestyle issue but as a chronic, treatable disease that warrants medical intervention.
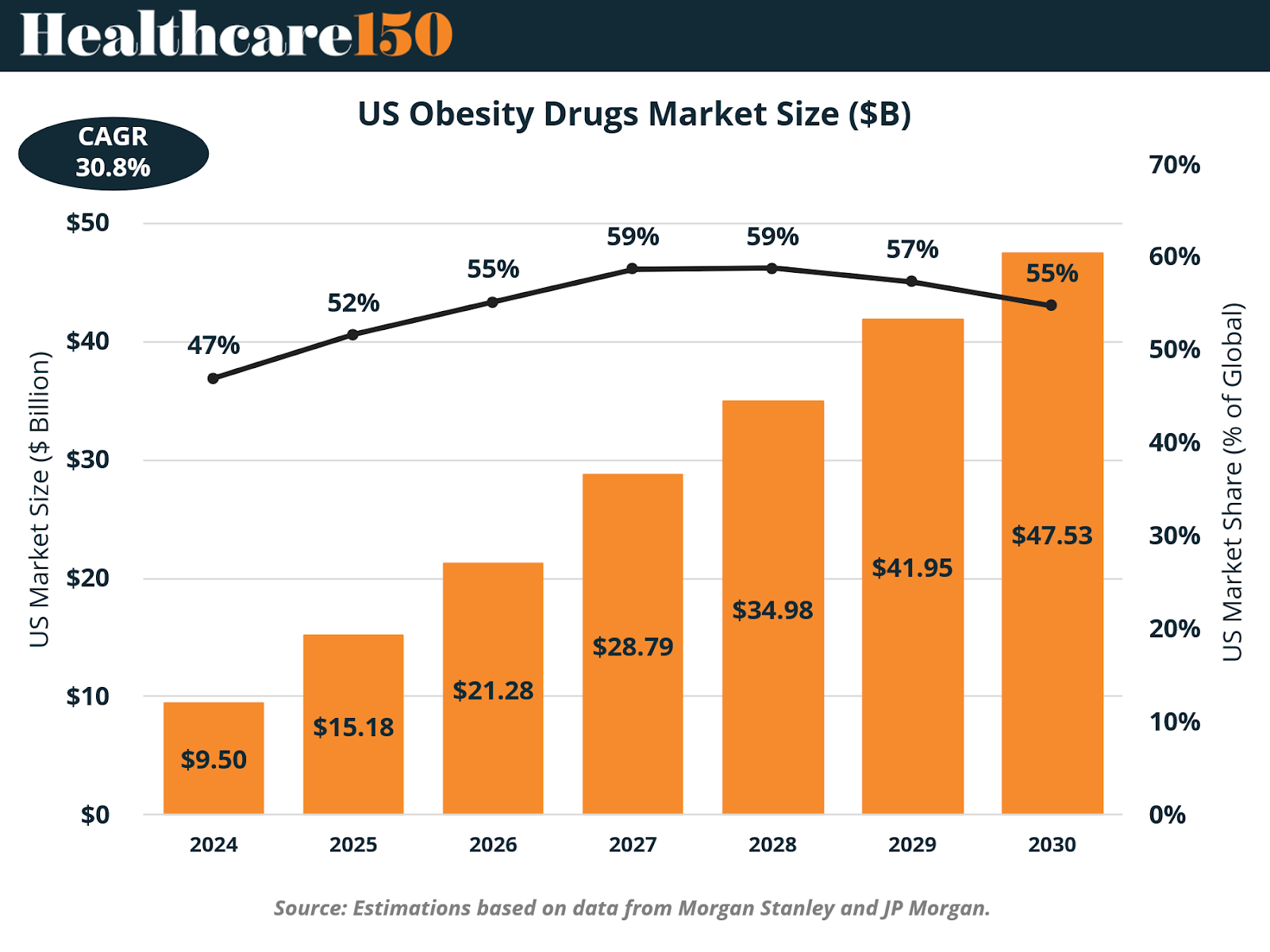
Nevertheless, the U.S. market faces key structural challenges. Insurance coverage remains uneven, with only about 55% of benefit leaders currently covering GLP-1-based drugs for weight loss. The removal of reimbursement and access barriers will be essential to sustain long-term growth and ensure equitable access to these transformative therapies.
Market Segmentation by Drug Type
The anti-obesity therapeutics landscape can broadly be divided into prescription drugs and over-the-counter (OTC) drugs. Prescription medications dominate this market, representing roughly 92% of total market share. This dominance is driven by the clinical success and regulatory approval of highly effective therapeutic agents targeting both central and peripheral mechanisms of obesity.
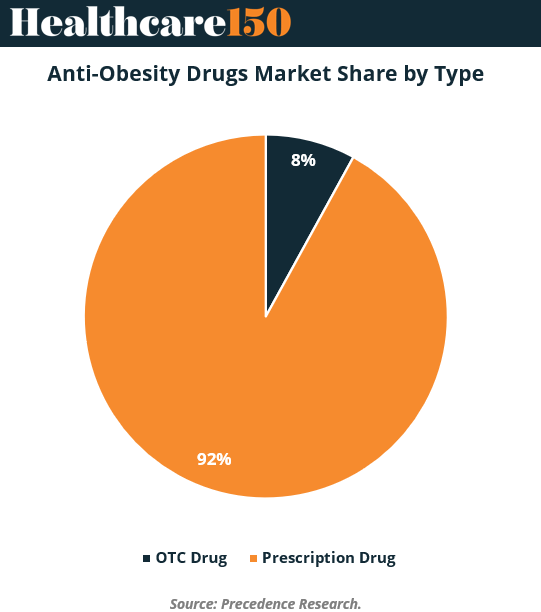
OTC drugs, while currently a smaller segment, are emerging as a significant growth frontier due to increasing consumer empowerment and digital accessibility. The rise of e-commerce and online pharmacies has made it easier for consumers to obtain non-prescription treatments for weight management. An example of this growing trend is Taisho Pharmaceutical’s launch of orlistat (Alli) in Japan in 2024—the first anti-obesity drug available without prescription in that country. This milestone underscores how consumer demand, convenience, and regulatory evolution are expanding access to obesity management solutions worldwide.
Epidemiological Context and Target Markets
The global obesity epidemic continues to intensify. The World Health Organization (WHO) projects that global obesity prevalence will increase from 14% in 2020 to 25% by 2035, affecting nearly 1.9 billion individuals. This surge in obesity is projected to cost the global economy $4 trillion annually, largely due to increased healthcare expenditures and productivity losses.
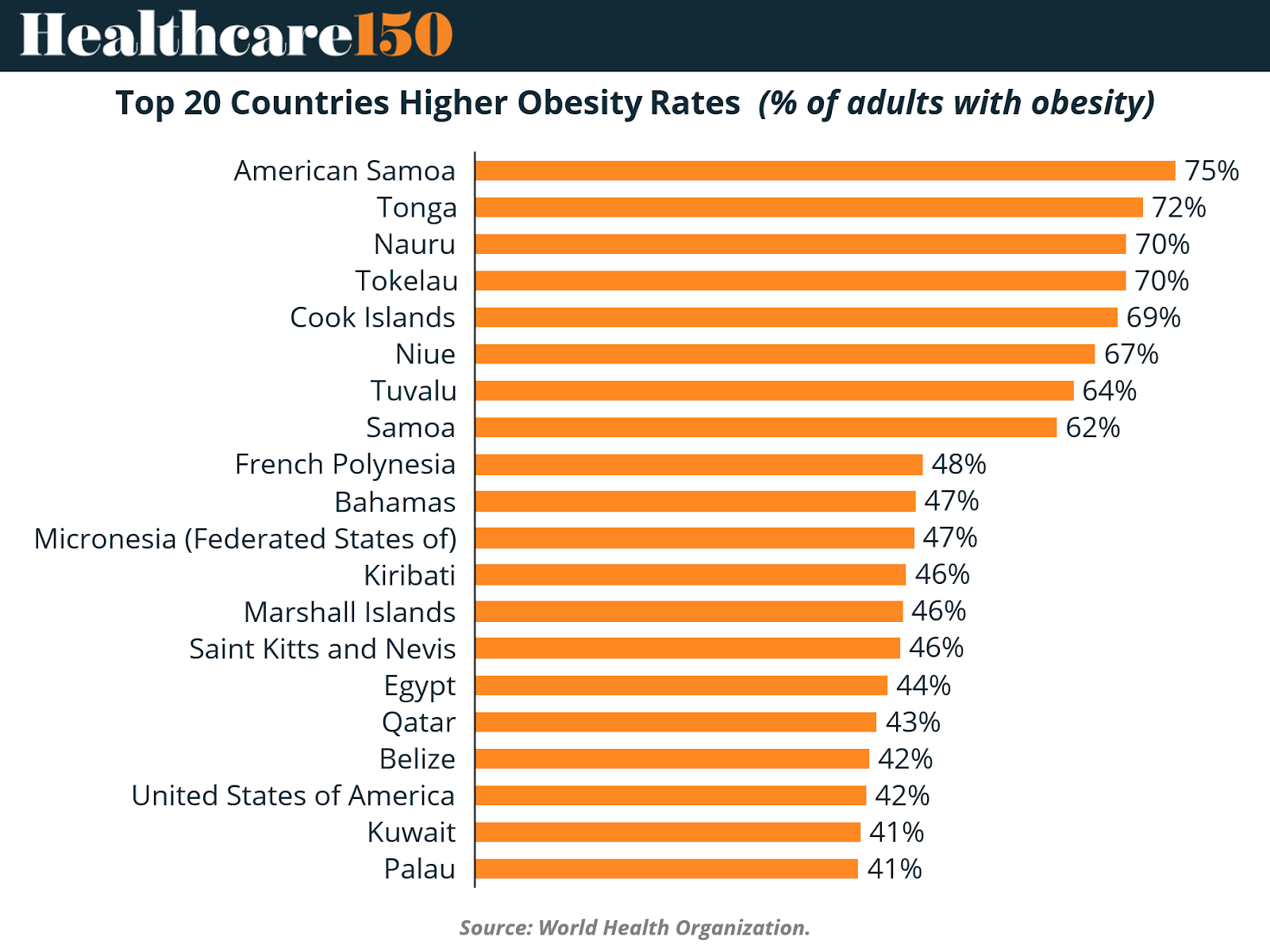
The countries with the highest obesity rates are predominantly found in the Pacific region, led by American Samoa, Tonga, and Nauru, where more than 70% of adults are obese. These are followed by other Pacific Island nations such as Tokelau, Cook Islands, and Niue, which also report alarming levels of obesity prevalence. Outside the Pacific, nations like Egypt, Qatar, and the United States also appear prominently, revealing how widespread the epidemic has become. The data highlight the need for coordinated, region-specific public health interventions alongside pharmaceutical innovation.
Market Opportunity Mapping
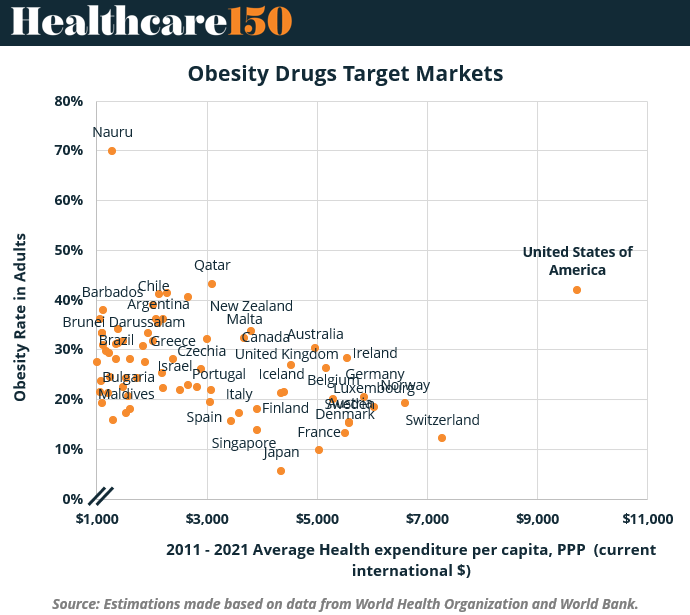
A comparative analysis of obesity prevalence and healthcare expenditure per capita provides valuable insights into target markets for obesity therapeutics. The United States stands out as the largest and most developed market, characterized by both high obesity rates and the world’s highest healthcare spending. This dual profile ensures robust market potential and sustained demand for advanced obesity treatments.
On the other hand, countries like Qatar, Argentina, and Nauru display high obesity prevalence but relatively moderate healthcare spending, suggesting unmet needs for affordable and accessible solutions. High-income nations such as Switzerland and Norway have low obesity rates but high healthcare expenditures, which could support early-stage interventions and preventive therapies. Meanwhile, emerging economies such as Brazil, Chile, and Greece are seeing steady increases in obesity rates while maintaining limited healthcare budgets, creating opportunities for scalable and cost-effective treatment approaches.
This intersectional analysis demonstrates that while the U.S. will remain the leading driver of obesity drug revenue, emerging and middle-income markets represent crucial avenues for global expansion and public health impact.
Key Market Drivers
A confluence of demographic, technological, and policy factors is accelerating growth in the obesity therapeutics market. Rising awareness about obesity’s impact on chronic disease, coupled with expanding treatment options, is driving adoption across both developed and emerging regions.
The growing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into medical practice is transforming obesity care through personalization and predictive analytics. AI-driven systems can analyze patient data to optimize treatment regimens, forecast response rates, and monitor real-time adherence. Machine learning algorithms also enable early detection of comorbidities through medical imaging, improving both prevention and treatment outcomes.
Government initiatives have become another vital growth engine. Many countries are launching policies and funding programs to combat obesity, expanding access to medical interventions and raising awareness. These efforts align with broader healthcare strategies focused on chronic disease prevention and lifestyle modification.
The pharmaceutical industry’s own advancements are equally critical. The introduction of GLP-1 receptor agonists and subsequent multi-agonists—targeting pathways like GIP, amylin, and glucagon—has revolutionized clinical outcomes. These therapies demonstrate remarkable weight loss efficacy and have shifted obesity from a cosmetic concern to a key therapeutic area.
Finally, the global economic rationale for obesity management is stronger than ever. Given obesity’s role in more than 200 chronic diseases, including diabetes and cardiovascular conditions, the reduction of obesity rates translates into long-term savings for healthcare systems. The combination of improved clinical outcomes and economic incentives has solidified obesity therapeutics as a central pillar of modern healthcare strategy.
Market Barriers and Challenges
Despite the strong growth outlook, the obesity therapeutics sector continues to face substantial challenges. One of the most pressing barriers is insurance coverage. In the United States, for instance, just over half of employers and insurers cover GLP-1-based therapies for weight loss. This limited reimbursement restricts access and slows adoption among lower-income populations.
The market also suffers from manufacturing and supply chain constraints. Surging demand for GLP-1 drugs has outstripped production capacity, leading to shortages and supply delays. These issues underscore the need for expanded manufacturing infrastructure and greater supply chain resilience.
In addition, safety and tolerability concerns remain. Although GLP-1 drugs are highly effective, adverse effects such as nausea and vomiting lead some patients to discontinue treatment prematurely. Pharmaceutical companies are addressing these challenges through combination regimens and novel formulations aimed at improving tolerability.
Finally, the market’s rapid growth has led to competitive saturation. The increasing number of entrants has raised concerns about product differentiation and pricing pressure, forcing companies to innovate beyond traditional GLP-1 mechanisms to maintain competitive advantage.
Dealmaking and Investment Trends
Strategic dealmaking has become a defining feature of the obesity therapeutics landscape. Between 2020 and 2025, more than $71 billion has been committed across 128 transactions, underscoring the sector’s status as one of the most dynamic in biopharma. The year 2024 alone accounted for $30 billion in alliances and acquisitions, reflecting investors’ growing confidence in the market’s long-term potential.
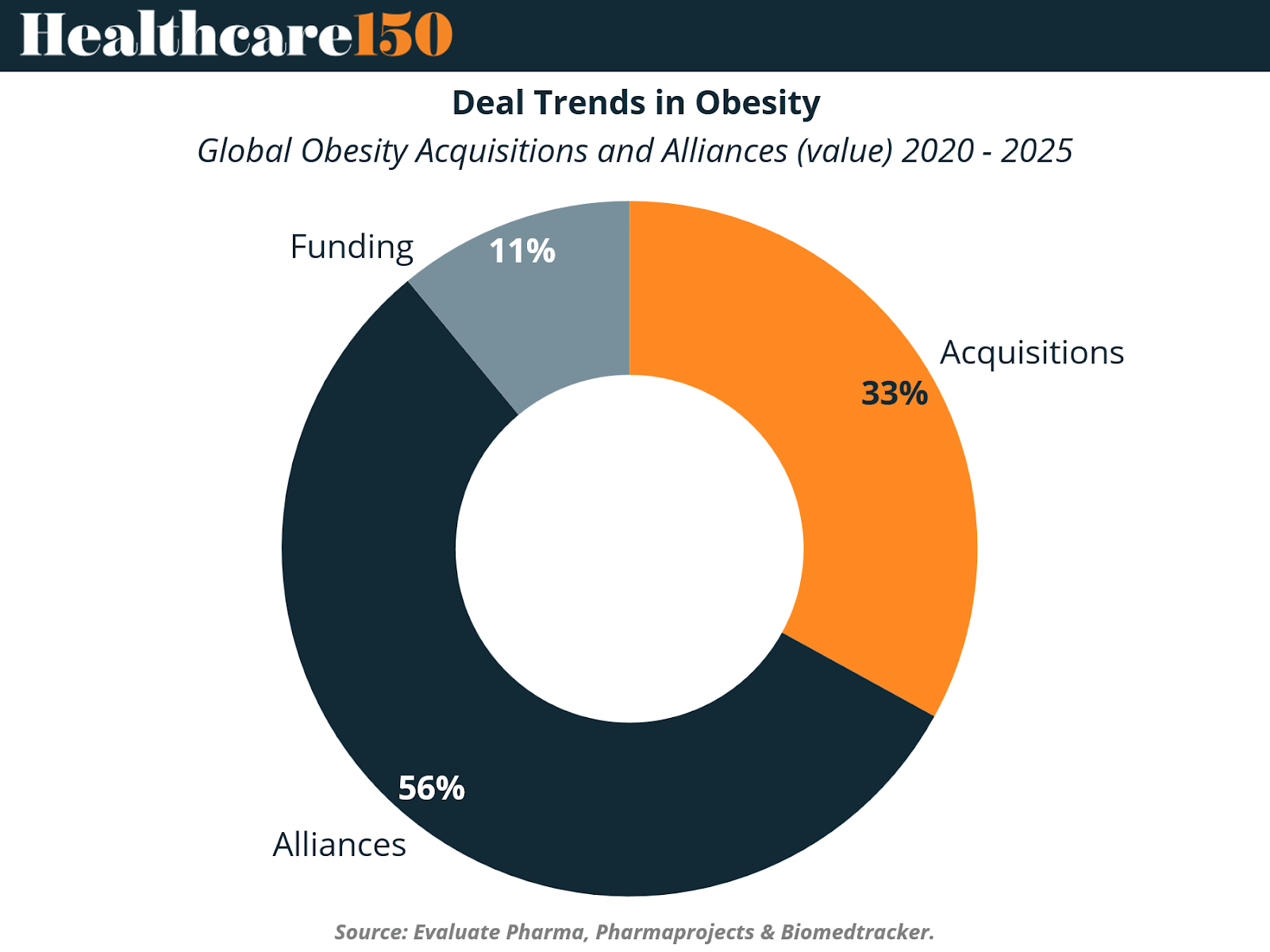
From 2020 to 2025, alliances represented the majority of transactions by volume, while acquisitions commanded the largest share of total deal value. This indicates a dual strategic approach by major pharmaceutical firms: building collaborative networks for early innovation while pursuing acquisitions to internalize the most promising assets. Funding arrangements, though smaller in number, have provided crucial capital for emerging biotech companies developing novel obesity treatments.
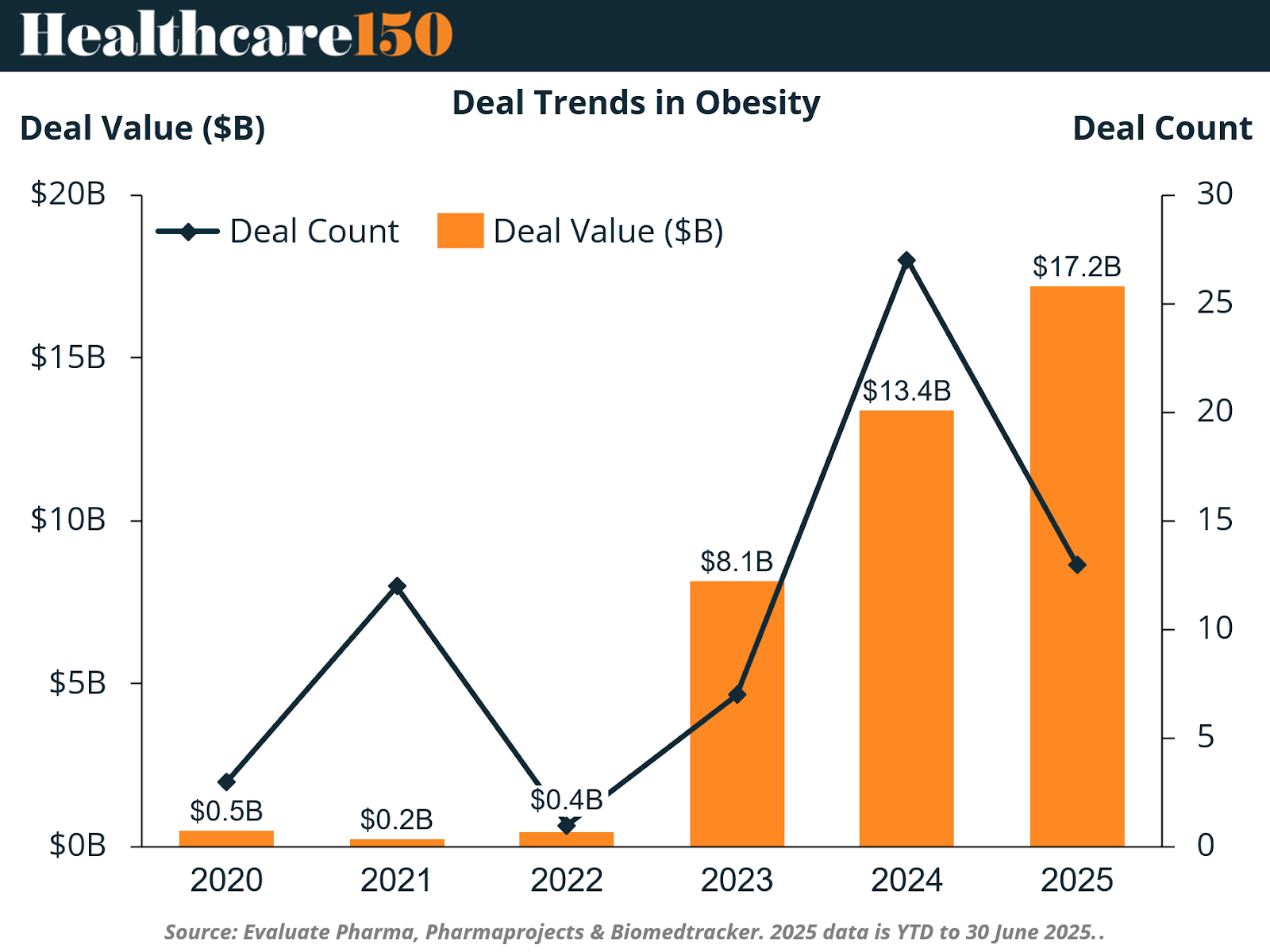
Deal values have increased dramatically over the past five years—from just $0.5 billion in 2020 to an estimated $17.2 billion in 2025. Major industry players such as Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer are driving this trend, building diverse portfolios through a mix of internal R&D and strategic partnerships. The consistent growth in deal size underscores the high stakes and escalating competition in the obesity drug market.
Development Stage Trends
Investment activity spans all phases of the development pipeline, but recent data show increasing focus on early and mid-stage programs. Investors are targeting discovery and platform-stage assets as long-term strategic bets to secure innovation pipelines for the next decade.
By mid-2025, Phase 2 programs alone had generated $5.7 billion in transactions, nearing the $7.5 billion total achieved in 2024. These programs offer a balance between manageable risk and near-term value, given that they often include proof-of-concept data. Late-stage (Phase 3) partnerships remain robust, with high-profile deals such as Regeneron and Hansoh’s $2 billion GLP-1/GIP agreement serving as benchmarks for valuation.
This balanced distribution of deal activity across early and late stages demonstrates investor confidence in both immediate commercial opportunities and long-term innovation.
Target and Mechanism Trends
GLP-1 remains the dominant target in obesity drug development, thanks to its proven efficacy and safety record. In 2024, incretin-based therapies, including GLP-1 and GIP agonists, accounted for 13 major deals worth $25.6 billion. However, the market is now diversifying beyond incretin pathways toward alternative mechanisms such as CB1 antagonists, MC4R agonists, and myostatin/activin inhibitors. These new targets are being pursued to address the limitations of GLP-1s, particularly concerning muscle preservation and gastrointestinal side effects.
Combination therapy represents another key evolution. Between 2024 and 2025, 13 major deals valued at $13.6 billion focused on multi-target regimens combining GLP-1s with agents such as amylin, myostatin, or calcitonin analogs. Examples include Roche and Zealand’s $5.25 billion Petrelintide co-commercialization, Regeneron and Hansoh’s $2 billion GLP-1/GIP plus anti-myostatin partnership, and AbbVie and Gubra’s $2.23 billion long-acting amylin licensing agreement. These transactions reflect a strategic pivot from monotherapies to more holistic treatment approaches designed to enhance efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Route of Administration Trends
The route of administration (RoA) is emerging as a critical differentiator in the obesity therapeutics market. Oral formulations now lead in deal volume, accounting for nearly 45% of all transactions over the past five years. This popularity stems from their convenience, lower cost, and improved patient adherence.
However, subcutaneous injectables continue to dominate in overall deal value, reaching $30.5 billion between 2024 and 2025. Injectable therapies remain the gold standard for achieving maximum efficacy, though ongoing innovation in oral GLP-1 formulations—such as MSD and Hansoh’s $2 billion licensing deal—illustrates strong momentum toward non-invasive delivery methods.
Oral treatments offer advantages beyond patient comfort; they simplify logistics, reduce cold-chain dependencies, and enable more flexible dosing, ultimately enhancing accessibility and compliance.
Regional Spotlight: China’s Expanding Role
China has rapidly emerged as a critical player in the global obesity therapeutics landscape. In 2024, out-licensing deals from Chinese firms totaled $9 billion, and projections indicate this figure will be surpassed in 2025. Currently, there are approximately 120 active obesity drug programs under development in China, spanning a range of mechanisms from GLP-1 and amylin analogues to entirely novel peptide classes.
This rise is driven by a potent combination of government investment, scientific talent, and demographic need. With an estimated 250 million overweight individuals expected by 2030, China’s domestic market presents enormous potential for local and international players alike. Moreover, the country’s ability to develop high-quality, cost-competitive biologics has made it an increasingly attractive partner for global pharmaceutical companies seeking collaboration and licensing opportunities.
Investment and Venture Funding Landscape
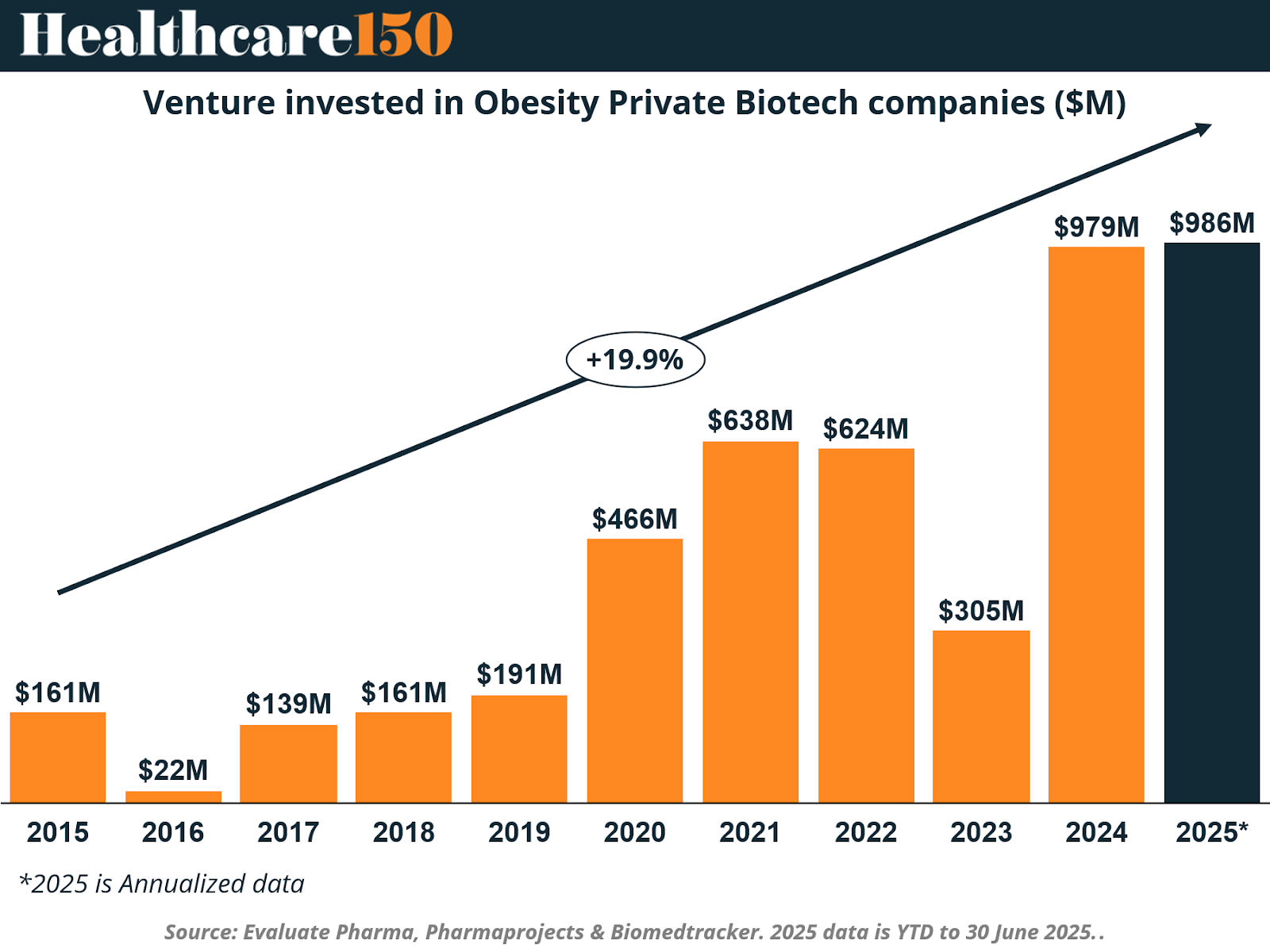
Investment in obesity-focused biotechnology has surged dramatically, rising nearly tenfold from 2019 to 2025. In 2025, venture investment is projected to reach $986 million on an annualized basis, underscoring the confidence investors have in the long-term profitability of this sector.
Venture capital, public offerings, and secondary share issues are all contributing to this financial influx, enabling early-stage companies to advance clinical development. Prominent mid-sized biopharma firms such as Zealand Pharma, Viking Therapeutics, and Structure Therapeutics have become major beneficiaries of this trend, advancing innovative compounds that promise to complement or outperform current GLP-1 therapies.
Broader Industry Impacts
The ripple effects of obesity therapeutics extend beyond pharmaceuticals into multiple sectors. Within healthcare, landmark trials like SELECT have demonstrated that GLP-1 drugs can reduce the risk of diabetes by 73% and cardiovascular events by 20%. These findings highlight their potential to transform chronic disease management, although longer patient lifespans may increase overall healthcare spending over time.
In the food and beverage industries, appetite-suppressing drugs are reshaping consumption habits. Consumers using GLP-1 therapies are eating less and shifting toward lower-calorie and healthier options. This trend may cause a 4% reduction in demand for sugary drinks, snacks, and alcohol by 2035, prompting companies to reformulate products, introduce smaller portion sizes, and emphasize health-oriented marketing.
The fitness industry, meanwhile, stands to gain significantly. Surveys indicate that patients using weight-loss medications are doubling their exercise frequency, leading to rising gym memberships, higher demand for athletic apparel, and greater engagement with digital fitness platforms. As more consumers pursue active lifestyles alongside pharmacological treatments, this synergy between fitness and medicine could redefine the health and wellness ecosystem.
Future Outlook
The obesity therapeutics market is poised to evolve into a multi-dimensional ecosystem combining pharmacology, technology, and behavioral science. Future developments will likely include expanded insurance coverage, wider adoption of AI-driven care models, and the rise of combination and oral therapies that improve patient convenience without compromising efficacy.
As major pharmaceutical firms continue to consolidate their obesity portfolios, mergers and acquisitions will further shape the competitive landscape. By 2035, obesity drugs are expected to account for nearly 9% of all global prescription drug sales, solidifying their role as a core therapeutic category comparable to oncology and diabetes.
Conclusion
The obesity therapeutics market is at a historic turning point. With market size projected to quadruple from $20.20 billion in 2024 to $86.71 billion by 2030, it has become one of the defining growth stories in modern healthcare.
The convergence of clinical innovation, investor enthusiasm, and societal awareness has transformed obesity treatment into a global priority. Yet, the success of this transformation will depend on addressing structural barriers such as reimbursement gaps, manufacturing constraints, and equitable global access.
As pharmaceutical companies, policymakers, and healthcare providers collaborate to tackle these challenges, obesity therapeutics will not only reshape the pharmaceutical landscape but also redefine the broader relationship between health, longevity, and lifestyle. This market is no longer a niche—it is a revolution at the heart of preventive and personalized medicine.
Sources & References
Evaluate Oharma. (2025). Obesity and GLP-1 Dealmaking: Strategic Trends and Market Signals. https://www.evaluate.com/thought-leadership/obesity-and-glp-1-dealmaking-strategic-trends-and-market-signals/?utm_campaign=EV-EVBRAND-202510-GLOB-Obesity%20and%20GLP-EM&utm_source=Eloqua&utm_medium=Email&utm_content=EV-EVBRAND-202510-GLOB-Obesity%20and%20GLP-EM-Email-1&utm_campaignID=701QP000012930NYAQ
JP Morgan. (2023). The increase in appetite for obesity drugs. https://www.jpmorgan.com/insights/global-research/current-events/obesity-drugs#section-header#0
Morgan Stanley. (2024). Scaling Up the Impact of Obesity Drugs. https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/obesity-drugs-market-expanded-opportunity
Morgan Stanley. (2023). Obesity Drugs Boost Pharma`s Growth Outlook. https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/obesity-drugs-investment-opportunity
Precedence Research. (2024). Anti-Obesity Drugs Market Size, Share and Trends 2024 to 2034. https://www.precedenceresearch.com/anti-obesity-drugs-market#:~:text=The%20global%20anti%2Dobesity%20drugs,5.53%25%20from%202024%20to%202034
World Bank. (2024). Current health expenditure per capita (current US$). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.XPD.CHEX.PC.CD
World Health Organization. (2024). Age-standardized prevalence of obesity among adults (18+ years). https://data.who.int/indicators/i/C6262EC/BEFA58B
World Obesity. (2023). Economic impact of overweight and obesity to surpass $4 trillion by 2035. https://www.worldobesity.org/news/economic-impact-of-overweight-and-obesity-to-surpass-4-trillion-by-2035
Premium Perks
Since you are an Executive Subscriber, you get access to all the full length reports our research team makes every week. Interested in learning all the hard data behind the article? If so, this report is just for you.
|
Want to check the other reports? Access the Report Repository here.
