- Healthcare 150
- Posts
- The evolving landscape of healthcare private equity
The evolving landscape of healthcare private equity
Healthcare has become one of the most dynamic and resilient sectors in the global private equity (PE) landscape.

In particular, the mid-market, typically defined as deal sizes ranging from $25 million to $1 billion, has emerged as a core segment for healthcare-related investments. This space offers unique opportunities for PE funds to scale businesses through consolidation strategies, digital transformation, and operational efficiency improvements, especially in fragmented subsectors such as outpatient services, behavioral health, specialty clinics, and healthcare IT.
Across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific and Latin America, mid-market healthcare deals have shown consistent growth, driven by aging populations, increasing demand for value-based care, and ongoing regulatory shifts. Notably, mid-market healthcare funds have delivered superior returns relative to large-cap peers, fueling robust fundraising. For instance, total capital raised by global mid-market healthcare funds grew by over 40% between 2019–2021 and 2022–2024, signaling continued investor confidence.
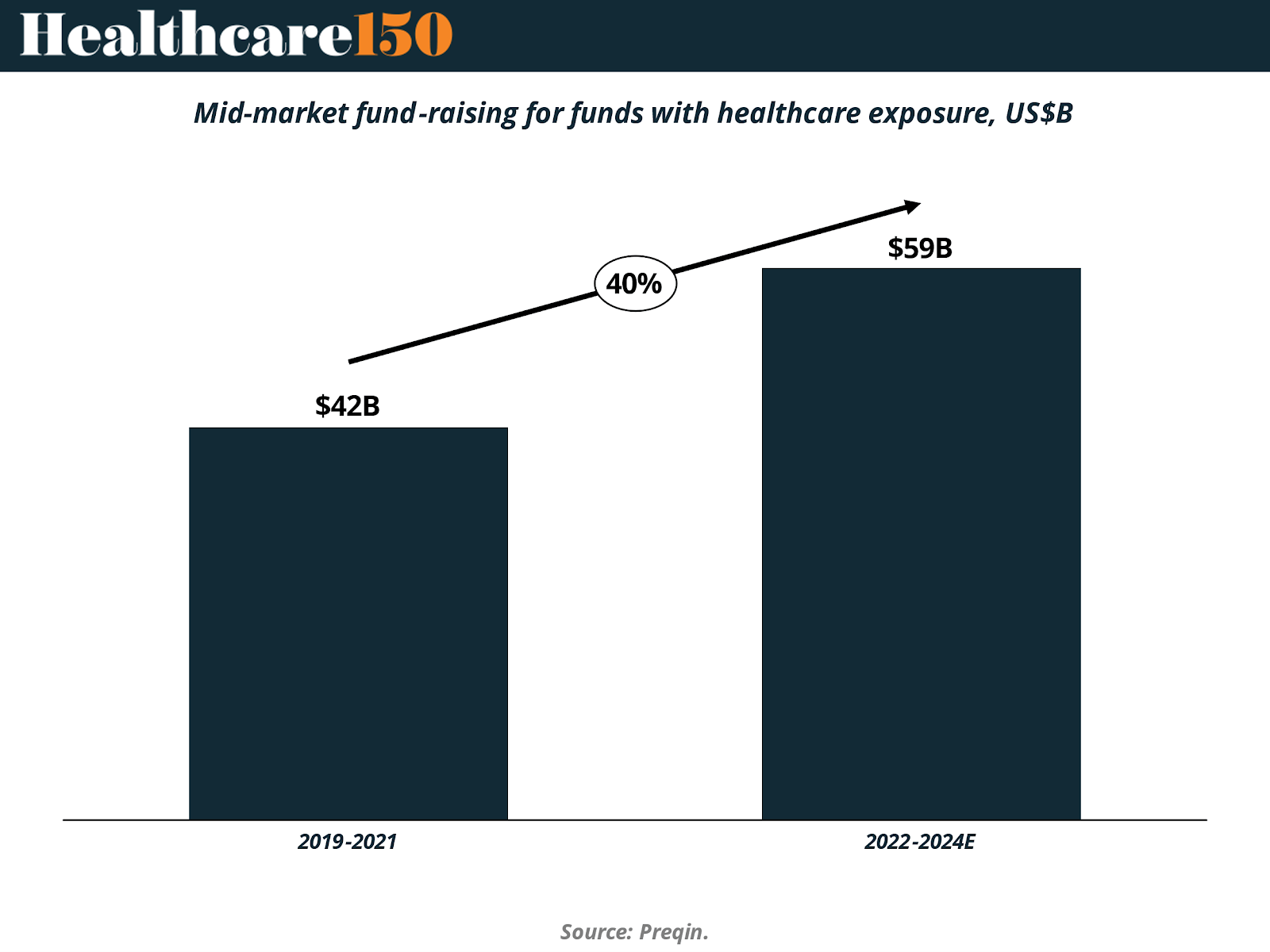
This momentum is further reinforced by macroeconomic trends expected to shape the 2025 investment landscape. Longer life expectancies and a rising prevalence of chronic conditions are putting sustained pressure on healthcare systems, creating a greater need for long-term services such as home health and specialized care. These conditions make certain healthcare niches particularly attractive for private equity investment, especially where scalable models and consolidation can improve both access and efficiency.
Simultaneously, the healthcare sector is still feeling the ripple effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cost pressures stemming from labor shortages, disrupted supply chains, and inflation remain a concern for providers. However, these challenges also present openings for investors to drive operational improvements, optimize cost structures, and implement technology-driven solutions at scale.
Regulatory change adds another layer of complexity and opportunity. Recent developments in areas such as physician practice ownership, reimbursement models, and telehealth regulation are shifting the landscape in multiple markets. While the regulatory environment varies by region and remains fluid, investors with a deep understanding of local dynamics can position themselves to benefit from policy transitions and the shift toward more integrated, value-focused care delivery models.
Together, these structural drivers are creating a dynamic and opportunity-rich environment for mid-market healthcare private equity, with attractive prospects for both financial returns and long-term sector transformation.
Mid-market deal activity: Steady growth amid cycles
To better understand the trajectory of healthcare private equity investment in the mid-market, the chart below illustrates annual deal count from 2007 to 2024, alongside healthcare’s share of total US PE mid-market activity.
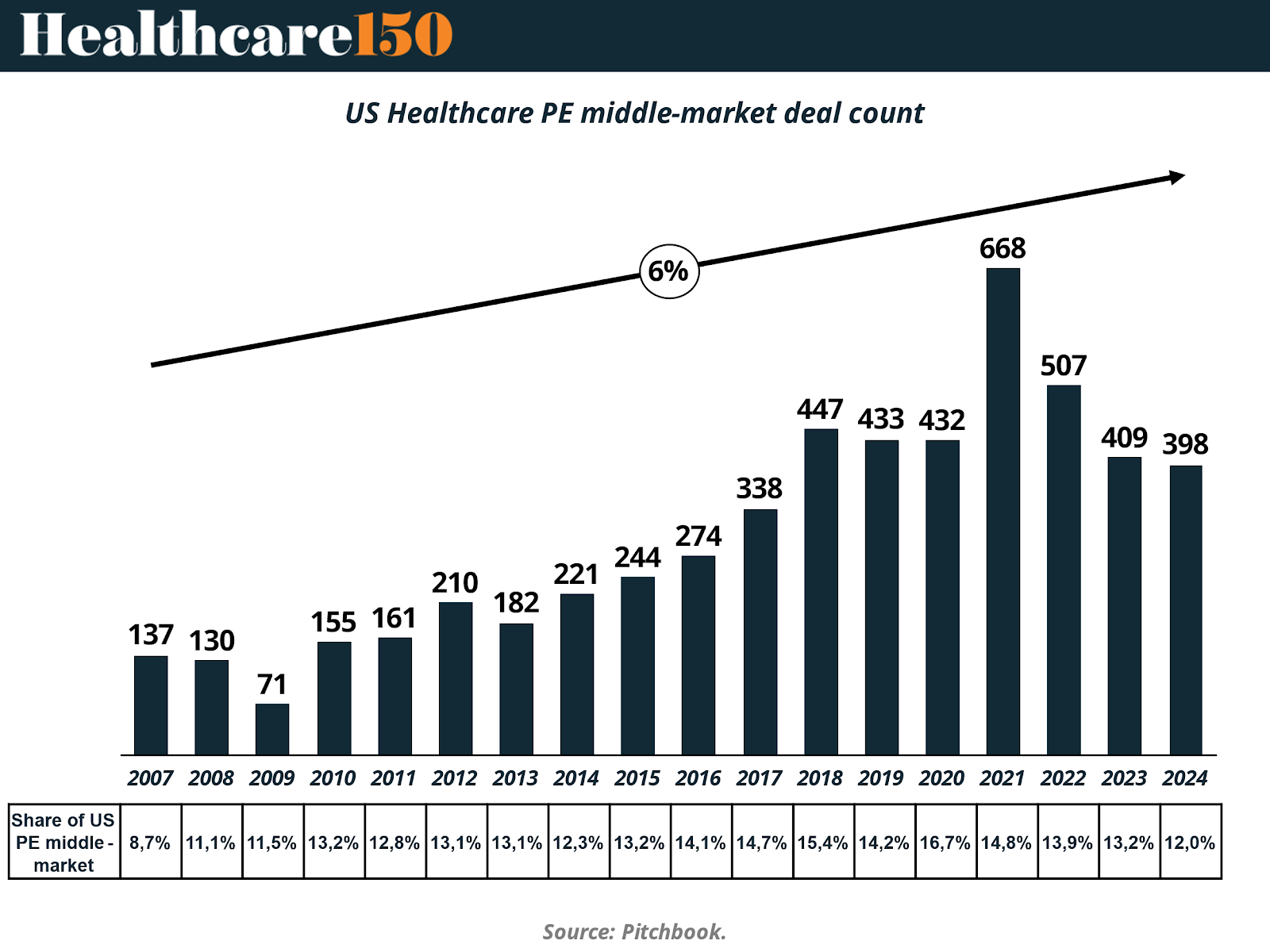
Over the past two decades, the US healthcare private equity mid-market has demonstrated a remarkable growth trajectory in deal activity. As illustrated in the chart above, annual deal count has increased more than fourfold, from just 137 transactions in 2007 to a peak of 668 in 2021, representing a compound annual growth rate of approximately 6%. Despite temporary fluctuations in 2022–2024, overall activity remains well above pre-2017 levels, highlighting the sector’s resilience even amid broader macroeconomic uncertainty and tightening credit conditions.
Importantly, the share of healthcare within the broader US PE mid-market universe has also expanded, from 8.7% in 2007 to peaks of over 16% in 2020 and 14.8% in 2021. Although this share moderated slightly in 2023–2024, the current 12% remains above long-term averages, suggesting that healthcare continues to be a relatively defensive and attractive sector for investors pursuing platform creation, roll-ups, and digital transformation plays.
This sustained level of activity underscores several secular drivers fueling the market, including demographic shifts, increasing chronic disease prevalence, demand for decentralized care delivery, and a growing number of tech-enabled services within healthcare. It also reflects the strategic advantage of the mid-market, where investors can execute add-on acquisitions and operational improvements more nimbly than in larger, more complex deals.
Exits in healthcare: Recent evolution and signs of recovery in 2024
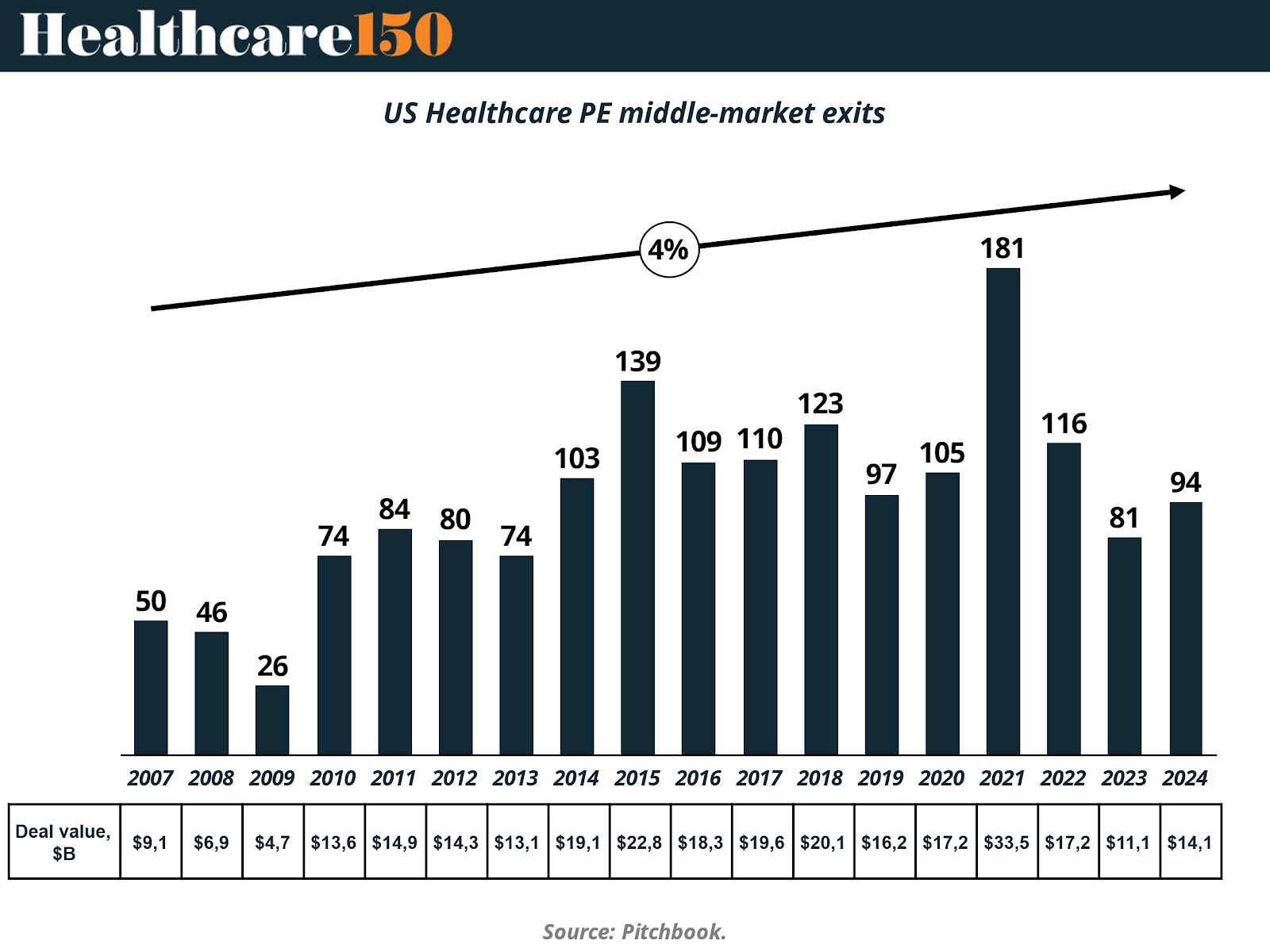
Between 2007 and 2024, the Healthcare sector has demonstrated solid dynamics in terms of exits within the private equity market. While activity hit lows during the global financial crisis of 2008–2009, the recovery was steady in the following decade, reaching a historic peak of 181 exits in 2021. This figure represents nearly seven times the level recorded in 2009, reflecting the increasing maturity and liquidity of the sector.
However, as in other industries, exit activity was negatively impacted in 2022 and 2023, amid tightening monetary policies, lower risk appetite, and a contraction in the IPO market. In this context, the number of exits dropped to 95 in 2023. Nevertheless, preliminary data for 2024 indicates a slight recovery, with 94 exits recorded to date, suggesting a gradual market rebound.
In terms of transaction values, the total deal value mirrored the general trend in exit volumes, with a peak of $33.5 billion in 2021, driven by high-ticket deals, strategic consolidations, and abundant liquidity. By 2024, the transaction value reached $14.1 billion, surpassing 2023 levels ($11.1 billion), reinforcing the perception of a more stable environment in the segment.
The chart below illustrates the annual evolution of the number of exits, while the complementary table details the total value of these transactions (in billions of dollars). Together, these elements highlight the strategic and resilient role of the Healthcare sector, which has managed to maintain relevant investment levels even in adverse economic cycle.
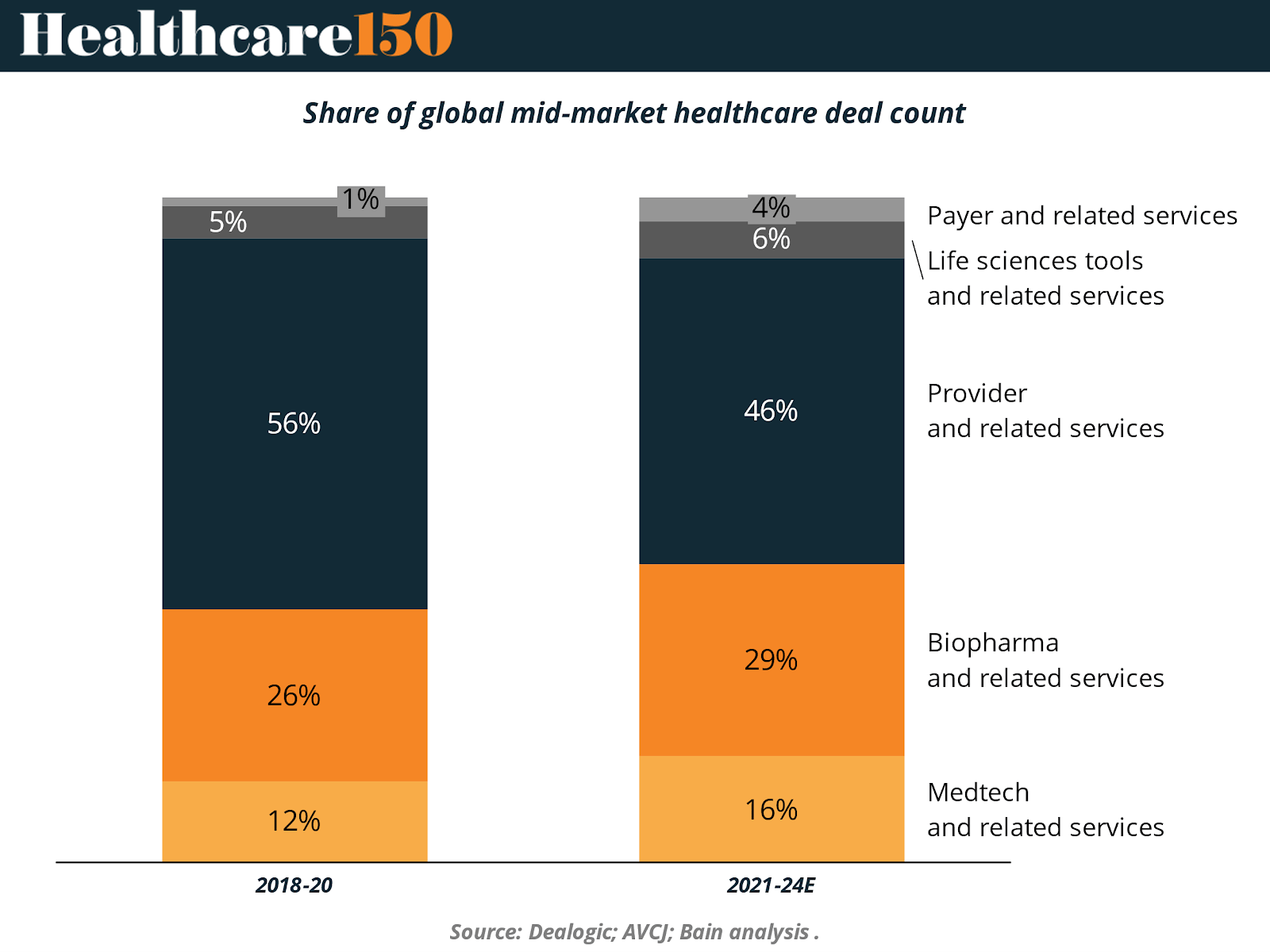
Emerging subsectors: Where mid-market capital is moving
As macroeconomic uncertainty and persistent labor challenges reshape the healthcare landscape, mid-market private equity investors are increasingly steering away from traditional provider models and toward subsectors that offer higher margins, operational leverage, and greater potential for digital enablement. This shift is particularly evident in the declining share of deals focused on core provider services, which historically represented the majority of mid-market healthcare investments. Since 2022, however, there has been a notable uptick in activity across ancillary services and healthcare IT, a trend that signals a deliberate pivot toward more scalable, tech-enabled business models that are less exposed to wage inflation and reimbursement pressure.
Healthcare IT has emerged as a particularly attractive vertical. Investors are actively targeting companies that offer digital infrastructure essential to modern care delivery, including platforms for revenue cycle management, workforce optimization, and patient access. These businesses typically generate recurring revenue, are embedded within clinical workflows, and offer clear metrics for return on investment, traits that align well with the value creation playbooks favored by mid-market sponsors.
Simultaneously, capital is flowing into biopharma services and medtech, two subsectors that combine technical complexity with favorable business fundamentals. These segments are gaining attention for their role in enabling the broader healthcare ecosystem, through services like contract development and manufacturing, clinical trial support, and compliance automation. Mid-market firms are backing platforms with deep domain expertise and the potential to scale through both digital enhancement and strategic M&A. Notable transactions include GI Partners’ investment in eClinical Solutions and WindRose’s backing of SubjectWell, each underscoring investor appetite for tech-forward enablers in life sciences.
Another area drawing sustained interest is decentralized care delivery, particularly ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) and home health services. As both payers and patients favor value-based, outpatient, and at-home models, PE investors are supporting operators that can deliver high-quality care more efficiently and at lower cost. These models also tend to offer clearer paths to regional scale and professionalization, key levers for growth in the mid-market.
In all these emerging subsectors, mid-market funds are not only injecting capital but also actively partnering with management teams to scale operations, introduce technology, and drive sustainable performance improvements.
Continued interest in biopharma and life sciences
Mid-market private equity activity in biopharma has maintained strong momentum since the 2021 deal surge, even as broader healthcare PE segments—including traditional mid-market provider deals—have slowed. Several specialized PE firms have developed deep domain expertise in biopharma and life sciences, enabling them to identify and close high-quality deals with greater conviction. This expertise allows them to assume technical risks that more generalist healthcare investors typically avoid.
These firms often focus on founder-owned businesses, helping to mitigate valuation challenges such as bid-ask spreads that are more common in other healthcare subsegments. Additionally, mid-market investors have expanded their scope beyond traditional biopharma and life science services to include companies involved in testing, inspection, certification, and compliance—areas critical to the broader healthcare ecosystem.
Supporting commercialization and healthcare IT has also become a key focus. Opportunistic investments in contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) have gained traction, reflecting the sector’s increasing complexity and technical demands. Notable 2024 transactions include WindRose Health Investors’ acquisition of SubjectWell and GI Partners’ purchase of eClinical Solutions, exemplifying a growing trend toward platform investments that enhance digital infrastructure and operational efficiency within biopharma.
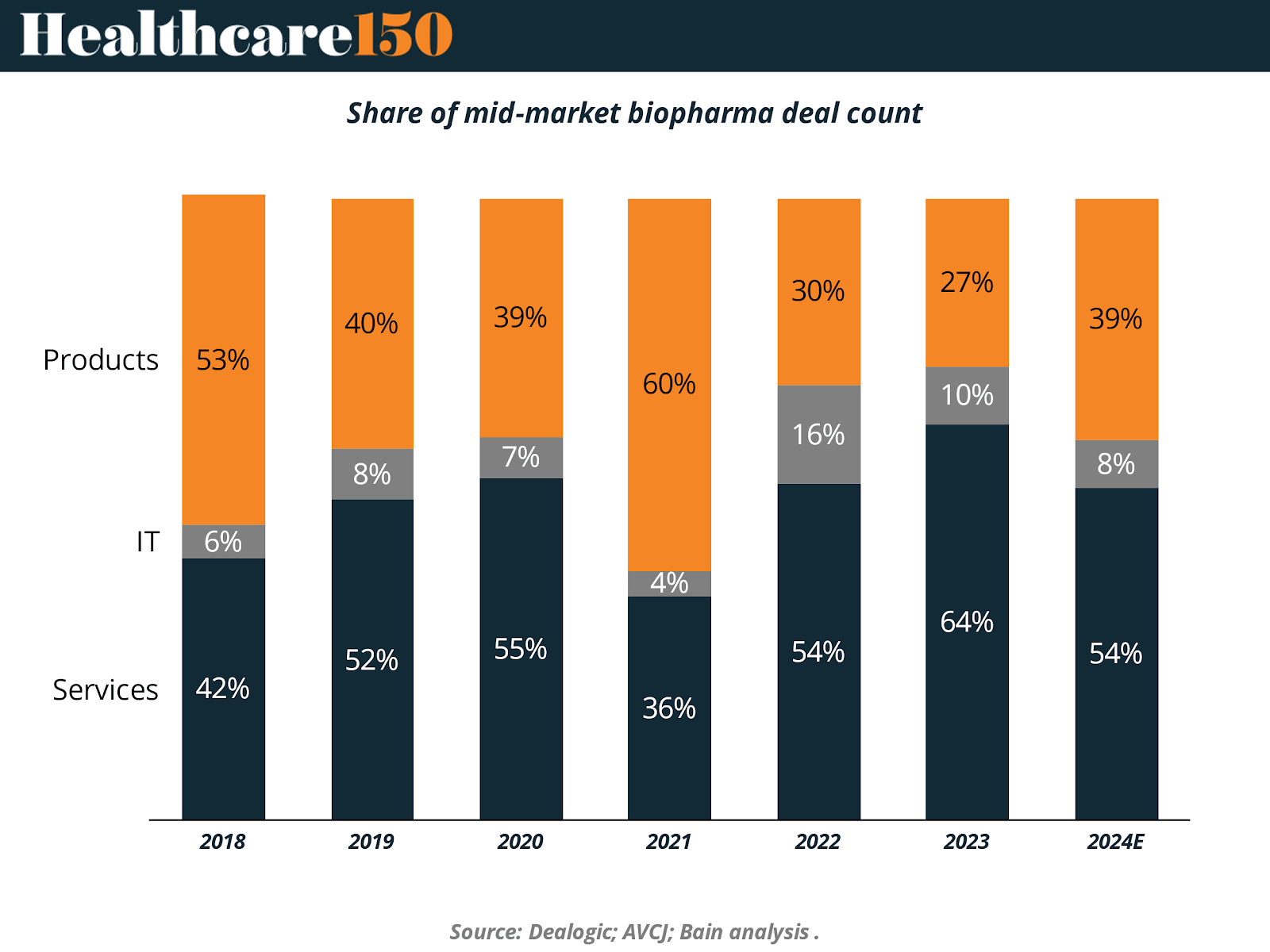
The accompanying chart illustrates how mid-market funds are shifting biopharma deal activity toward IT and services, with the share of deals targeting these areas growing significantly over recent years. This evolution highlights the sector’s ongoing transition away from traditional product-oriented investments and toward technology-enabled and service-based business models.
Moving beyond scale: The next phase of value creation
While buy-and-build strategies have long been a cornerstone of mid-market private equity in healthcare, today’s environment demands a more nuanced approach. Historically, many firms have generated substantial returns by executing roll-up strategies, leveraging tuck-in acquisitions to achieve multiple expansion and operational synergies. This model has been particularly effective in fragmented provider segments. However, in the face of rising interest rates, compressed exit timelines, and intensifying competition, relying solely on scale is no longer sufficient.
Investors are increasingly prioritizing broader value-creation levers beyond consolidation. These include centralizing infrastructure, enhancing operational capabilities, and expanding service capacity, all of which are crucial to unlocking sustainable growth and margin improvement. The most effective strategies are no longer generic but must be tailored to each asset and subsegment. For example:
Physician Practices: Specialty medical groups are extending into adjacent ancillary services, such as ambulatory surgery centers in cardiology, genetic testing labs in fertility, or integrated radiology services in orthopedics. Operational efficiencies can also be captured through the centralization of billing, procurement, IT systems, and clinical workflow optimization. These initiatives not only enhance patient experience but also boost provider productivity and profitability. Furthermore, practices that adopt value-based care (VBC) models, albeit at varying levels of maturity, can unlock new reimbursement pathways and long-term performance incentives.
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and CDMOs: PE-backed platforms in life sciences services are scaling by investing in new capacity, expanding technical capabilities (e.g., specialized materials or production methods), and acquiring complementary businesses. These strategies help improve cost structures, bolster efficiency, and meet the rising demand for integrated solutions across the drug development value chain.
Healthcare IT: Companies in this segment benefit from scale through reduced technology debt and improved operational resilience. Larger platforms are also better positioned to invest in new product features and adjacent digital offerings, increasing stickiness and expanding their total addressable market.
To thrive in today’s environment, mid-market sponsors must also enhance their internal expertise. This includes integrating generative AI into their investment and operational playbooks, building deep domain knowledge in highly technical verticals such as biopharma, and navigating complex reimbursement and economic models, such as the buy-and-bill dynamics in oncology practices.
Limited Partners (LPs) continue to view mid-market healthcare funds as a source of innovation and strong historical performance. However, sustaining that edge requires deeper specialization, robust operational engagement, and a thoughtful approach to asset transformation. As macroeconomic headwinds challenge traditional exit paths, firms that succeed will be those with a clear vision for long-term value creation, both at the asset and portfolio level.
The rising opportunity in home infusion therapy and home-based care for id-market healthcare private equity
Home infusion therapy and home-based care services represent one of the fastest-growing and most attractive segments in the mid-market healthcare private equity (PE) landscape. This growth is driven by demographic shifts, increasing chronic disease prevalence, technological advancements, and evolving patient preferences toward receiving care in the comfort of their own homes.
The global home infusion therapy market is projected to grow significantly over the next decade. Estimates indicate the market size will reach approximately USD 26 billion in 2025 and expand to over USD 41 billion by 2032, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.8%. More aggressive forecasts suggest the market could grow even faster, with projections reaching USD 52.8 billion by 2029 at a CAGR above 10%. In the United States alone, the home infusion therapy market is expected to nearly double from USD 10.3 billion in 2024 to more than USD 20.5 billion by 2033, growing at an 8% CAGR.
Several factors underpin this rapid expansion. The aging global population and the rising incidence of chronic illnesses—such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular, and autoimmune diseases—are increasing the demand for long-term, cost-effective treatment options that can be administered outside hospital settings. Home infusion therapy allows patients to receive intravenous medications, nutrition, and other therapies safely at home, reducing hospital stays and healthcare costs while improving patient comfort and quality of life.
Technological advancements in infusion devices, including portable and smart infusion pumps with remote monitoring capabilities, are enhancing patient safety and compliance, further accelerating adoption. Additionally, the integration of telehealth services and value-based care models supports the shift toward decentralized care delivery, which aligns well with private equity strategies focused on scalable, recurring-revenue healthcare platforms.
The home infusion sector remains highly fragmented, presenting attractive opportunities for mid-market PE firms to consolidate providers, professionalize operations, and drive value creation through operational improvements and technology enablement. The relatively lighter regulatory environment compared to hospital-based care also facilitates faster growth and higher margins.
Moreover, the increasing patient preference for home-based care, driven by convenience and pandemic-related hospital avoidance, is expected to sustain demand growth. This trend is complemented by payers’ interest in cost containment, making home infusion therapy a win-win for patients, providers, and investors.
In summary, home infusion therapy and home-based care services offer mid-market healthcare private equity investors a compelling combination of strong market growth, favorable demographic and clinical trends, technological innovation, and attractive consolidation opportunities. As healthcare continues to shift toward patient-centric, decentralized models, these segments stand out as key drivers of value and transformation in the healthcare PE landscape.
Conclusion
The evolution of healthcare private equity, particularly in the mid-market, reflects both the sector’s resilience and its capacity for transformation. As this report has demonstrated, sustained demographic trends, regulatory shifts, and technological advancement are converging to reshape the landscape of healthcare investing. Mid-market funds have consistently capitalized on this momentum by embracing tailored strategies that go beyond traditional consolidation, instead focusing on value creation through digitization, operational improvement, and sector specialization.
Investor interest continues to migrate toward high-growth, high-margin subsectors such as healthcare IT, biopharma services, decentralized care, and ancillary solutions. These verticals offer structural advantages, scalability, defensibility, and embedded value creation mechanisms, that are increasingly important in a capital-constrained, post-COVID world. Meanwhile, the traditional provider segment is undergoing its own reinvention, with players exploring adjacent service lines, value-based care models, and back-office optimization to maintain relevance and improve returns.
Importantly, the success of mid-market sponsors in the next phase will hinge on their ability to deepen domain expertise, engage operationally with portfolio companies, and deploy technology, such as AI and automation, as enablers of performance. Generalist approaches are giving way to specialist investment theses, and executional excellence will become a key differentiator in a more competitive fundraising and exit environment.
As we look ahead to 2025 and beyond, mid-market healthcare private equity is well positioned to continue outperforming, driven by long-term tailwinds, increased investor sophistication, and a growing emphasis on purposeful, sustainable growth. For fund managers, operators, and limited partners alike, the opportunity lies not only in identifying the next platform, but in building it with precision, foresight, and value creation at its core.
Sources and References:
Bain – Mid-Market Healthcare Private Equity in 2025 (PDF)
Bain – Why Mid-Market Healthcare Private Equity Firms Are Outperforming
Dimensional Insight – Private Equity Landscape in Healthcare in 2025
ECA Partners – PE Outlook 2025: Multisite Healthcare & Leadership Talent
Bain – Global Healthcare Private Equity Report 2025: Year in Review & Outlook
GlobeNewswire – US Home Infusion Market Forecast 2025–2033
Coherent Market Insights – Home Infusion Therapy Market Overview
Premium Perks
Since you are an Executive Subscriber, you get access to all the full length reports our research team makes every week. Interested in learning all the hard data behind the article? If so, this report is just for you.
|
Want to check the other reports? Access the Report Repository here.
