- Healthcare 150
- Posts
- Precision Medicine at Scale: From Genomic Investment to System-Wide Impact
Precision Medicine at Scale: From Genomic Investment to System-Wide Impact
How sustained funding, advanced analytics, and decentralized care models are transforming precision medicine from a clinical innovation into a foundational healthcare paradigm.

I. Introduction
Precision medicine represents one of the most consequential shifts in modern healthcare: the move away from standardized treatment pathways toward care models tailored to individual biological and clinical profiles. As healthcare systems confront rising costs, variable patient outcomes, and declining efficiency in one-size-fits-all therapies, precision medicine has emerged as a structural response, promising more accurate diagnoses, better treatment matching, and improved clinical outcomes.
While the applications of precision medicine are most visible in areas such as oncology, rare diseases, and pharmacogenomics, its scalability depends on a less visible but critical foundation: sustained investment in human genome research. Genomic data enables clinicians and researchers to identify biomarkers, stratify patient populations, and predict therapeutic response, capabilities that define precision care in practice rather than theory.
Over the past decade, funding trends underscore the growing institutional commitment to this model. Total human genome funding by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has increased from approximately $2.9 billion in FY2015 to more than $5.2 billion projected for FY2025, nearly doubling in size. Importantly, funding accelerated after 2020, signaling a strategic shift toward treating genomic infrastructure as a core healthcare asset, not a peripheral research expense.
This expansion in funding has enabled the development of large-scale sequencing programs, population-level genomic databases, advanced bioinformatics platforms, and clinical validation pipelines, all essential for translating precision medicine from research environments into routine care. Rather than driving innovation in isolation, genomic funding acts as a force multiplier, supporting downstream advances across diagnostics, targeted therapeutics, AI-driven decision support, and personalized treatment pathways.
The relationship is not immediate, but it is structural. Increases in genome funding precede and to a large extent determine, the pace at which precision medicine can be deployed at scale. As healthcare organizations seek solutions that improve outcomes while controlling costs, precision medicine’s viability increasingly rests on the depth, quality, and accessibility of genomic infrastructure.
This report explores the precision medicine landscape through that lens: examining how sustained investment in human genomics has enabled today’s clinical applications, shaped adoption pathways, and set the stage for future growth across healthcare systems.

II. Precision Medicine Market Size
The precision medicine market is transitioning from early adoption to a scalable growth phase, supported by expanding clinical use cases, improving reimbursement pathways, and maturing genomic and data infrastructures. What began as a niche segment concentrated in oncology and rare diseases is increasingly permeating broader areas of healthcare delivery, signaling a structural expansion rather than episodic growth.
The global precision medicine market is projected to grow from approximately $119 billion in 2025 to over $470 billion by 2034, representing a nearly 4x expansion over the period. This trajectory implies a sustained high-teens to low-20s compound annual growth rate, positioning precision medicine among the fastest-growing segments within the broader healthcare ecosystem.
Importantly, this growth is not driven by a single product category or therapy class. Instead, it reflects the cumulative contribution of multiple layers of the precision medicine stack, including genomic and molecular diagnostics, companion diagnostics, targeted therapeutics, data analytics platforms, and clinical decision support tools. As these components become more tightly integrated into care pathways, precision medicine shifts from being additive to foundational within clinical workflows.
The steepening of the growth curve post-2028 is particularly notable. This inflection aligns with broader system-level enablers discussed earlier in the report, namely, expanding genomic datasets, declining sequencing and analysis costs, and increased provider familiarity with biomarker-driven treatment protocols. As a result, precision medicine adoption is increasingly driven by operational efficiency and outcome optimization, not only by clinical novelty.
From a healthcare system perspective, the market’s expansion also reflects a reframing of value. Precision medicine supports better patient stratification, reduced trial-and-error prescribing, and improved treatment response rates, which translate into lower downstream costs and more predictable outcomes. These economic incentives are critical in enabling precision-based approaches to scale beyond specialized centers into routine care settings.
Overall, the projected growth of the precision medicine market underscores a decisive shift: precision medicine is no longer emerging, it is becoming embedded. As genomic infrastructure, analytics, and targeted therapies converge, precision medicine stands to redefine how value is created and captured across healthcare over the next decade.
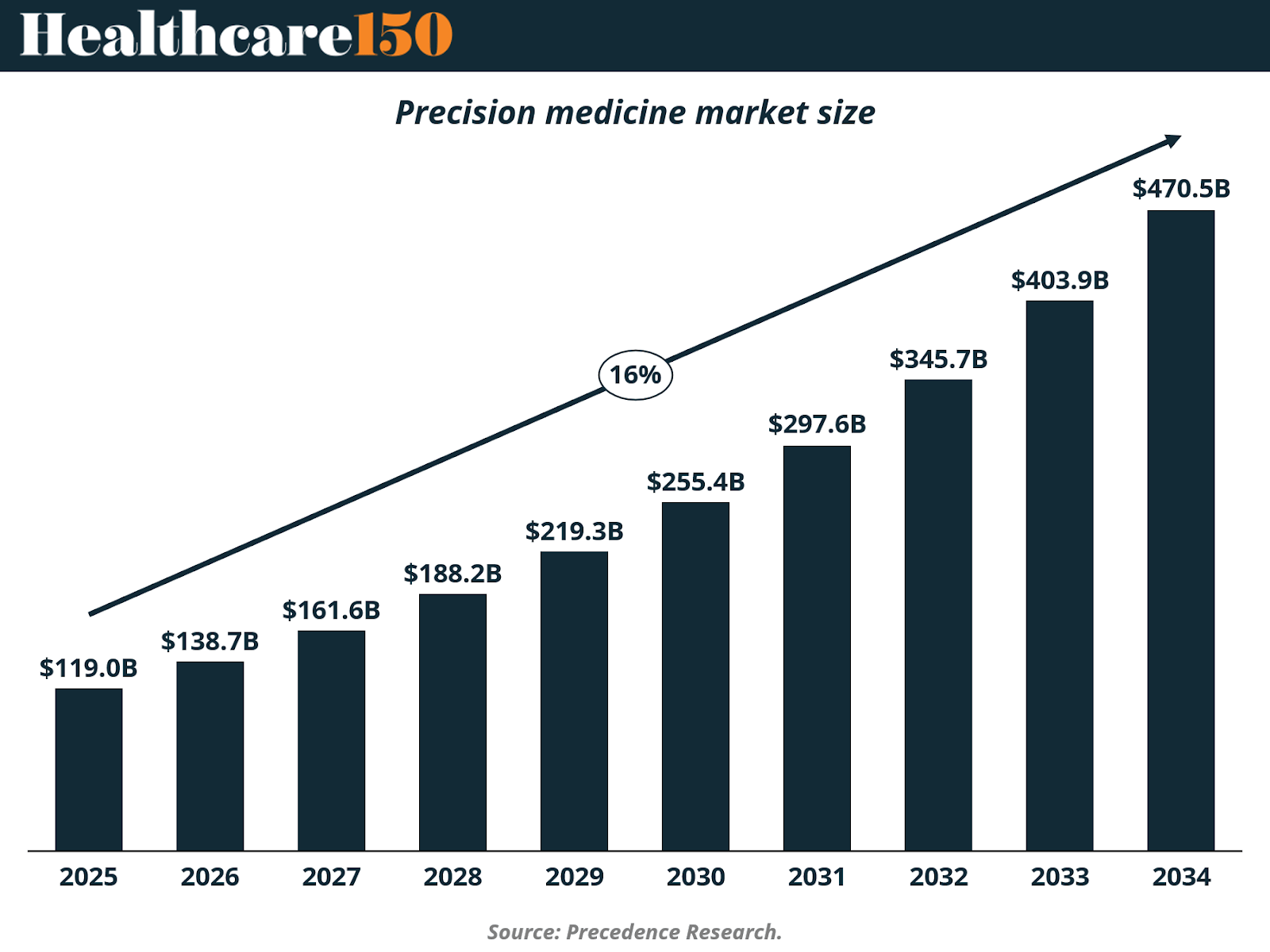
III. Regional Breakdown: Precision Medicine Adoption Is Concentrated, but Expanding
The precision medicine market remains highly concentrated geographically, reflecting disparities in healthcare infrastructure, genomic research capacity, reimbursement frameworks, and clinical adoption readiness. As of 2024, North America accounts for the clear majority of global precision medicine revenues, but regional diversification is accelerating as genomic capabilities expand globally.
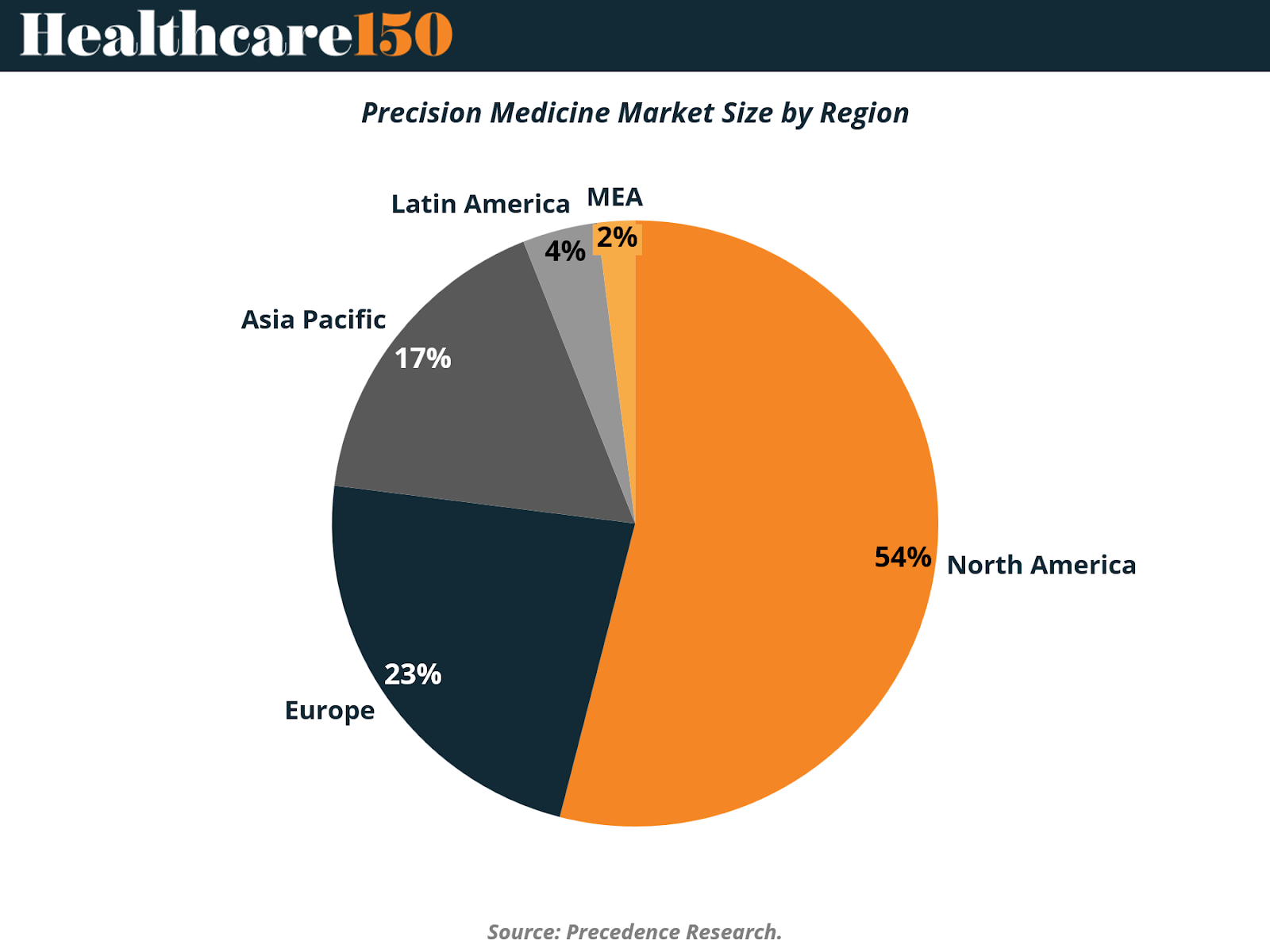
North America represents approximately 54% of the global precision medicine market, maintaining its position as the sector’s epicenter. This dominance is driven by a combination of factors: deep federal and private investment in genomics, early adoption of biomarker-driven treatments, mature reimbursement mechanisms, and strong alignment between academic research, biopharma, and healthcare providers. The region’s leadership also reflects its ability to translate genomic research into routine clinical practice at scale, particularly in oncology and rare diseases.
Europe follows with a 23% market share, supported by robust public healthcare systems, coordinated research initiatives, and growing regulatory support for personalized therapies. While adoption varies by country, EU-wide genomics programs and cross-border data initiatives are strengthening Europe’s position as a precision medicine innovation hub. However, reimbursement variability and slower clinical integration in certain markets continue to temper near-term growth relative to North America.
The Asia-Pacific region accounts for approximately 17% of the market, representing one of the most strategically important growth frontiers. Governments across China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are investing heavily in population-scale genomic programs, digital health infrastructure, and AI-enabled diagnostics. Although overall penetration remains lower than in Western markets, Asia-Pacific’s large patient populations and accelerating investment cycles position the region as a key driver of future precision medicine expansion.
In contrast, Latin America (4%) and the Middle East & Africa (2%) together comprise a relatively small share of the global market. In these regions, adoption is constrained by limited genomic infrastructure, lower sequencing penetration, and fragmented reimbursement systems. That said, targeted investments, pilot programs, and public–private partnerships are beginning to establish foundational capabilities, particularly in urban and private-care settings.
Overall, the regional distribution of the precision medicine market underscores a critical dynamic: while adoption today is concentrated in advanced healthcare systems, future growth will increasingly depend on geographic expansion, localization of genomic infrastructure, and policy-led investment in emerging markets. As precision medicine matures, narrowing this regional gap will be essential to unlocking its full global potential.
IV. U.S. Market Size & Dynamics: The Core Engine of Precision Medicine Growth
The United States represents the single most important market for precision medicine, serving as both the largest revenue contributor and the primary engine of clinical and commercial innovation. Its leadership reflects not only market scale, but also depth of adoption across diagnostics, therapeutics, and data-driven care models.

The U.S. precision medicine market was valued at approximately $58.1 billion in 2025 and is projected to exceed $232.5 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.66% over the period. This nearly 4x expansion underscores the country’s outsized role in translating precision medicine from research-driven innovation into scaled healthcare delivery.
Growth in the U.S. market is supported by a uniquely mature ecosystem. The country benefits from robust venture and private equity funding, a dense network of academic medical centers, and a highly developed biotechnology sector that accelerates the commercialization of genomic diagnostics and targeted therapies. In parallel, regulatory frameworks, particularly around adaptive approvals and companion diagnostics (CDx), have enabled faster clinical validation and market entry relative to other regions.
Clinically, the U.S. remains the global leader in precision medicine–related clinical trials, biotech R&D, and real-world deployment of biomarker-driven treatment pathways. Adoption is especially strong in oncology, where targeted therapies, liquid biopsies, and molecular profiling are increasingly embedded in standard-of-care protocols. Active development of pharmacogenomics, rare disease diagnostics, and AI-enabled clinical decision support further reinforces the market’s depth.
Despite these strengths, the U.S. market faces meaningful structural challenges. Payer fragmentation, variable coverage policies, and high therapy prices continue to create access disparities and reimbursement uncertainty. However, these constraints have also catalyzed innovation in payment models, including outcomes-based contracts and pilot reimbursement frameworks for high-value precision interventions, signaling a growing willingness to align cost with clinical impact.
More broadly, North America captured the largest share of global precision medicine revenues in 2024 and is expected to maintain its dominance through the next decade. This leadership is driven by rising cancer prevalence, increased approval of personalized therapies, favorable government initiatives, and sustained investment in disease-specific genomic solutions. The U.S., in particular, functions as the reference market where regulatory precedent, reimbursement norms, and commercialization strategies are often established before diffusing globally.
As a result, U.S. market dynamics will remain critical not only to domestic growth, but to the global trajectory of precision medicine adoption. The pace at which the U.S. resolves reimbursement, pricing, and access challenges will materially influence how rapidly precision medicine scales worldwide.
V. Market Segmentation by Technology
Technology adoption within precision medicine reflects a two-layer ecosystem: data generation anchored in sequencing technologies, and value creation increasingly driven by advanced analytics. In 2024, this structure is clearly visible in market share allocation, with next-generation sequencing (NGS) and data-driven platforms, including AI and machine learning, commanding the majority of industry activity.

In 2024, next-generation sequencing (NGS) accounted for 34.24% of the precision medicine technology market, anchoring most companion diagnostics, tumor profiling assays, and pharmacogenomic workflows. NGS leadership was reinforced by the FDA clearance of Illumina’s TruSight Oncology Comprehensive assay, capable of profiling more than 500 biomarkers in a single run, cementing its status as the gold standard for broad genomic interrogation. Integrated cloud bioinformatics pipelines now process sequencer output in near real time, enabling clinicians to review actionable variants within a single visit.
However, the largest share of the market, 65.8%, is held by the combined segment of Big Data analytics, AI-enabled bioinformatics, clinical decision-support platforms, and other digital technologies. These tools form the computational backbone that transforms raw genomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and epigenomic data into clinically usable insights. Big Data infrastructure supports multimodal data harmonization, real-time clinical integration, and population-scale risk modeling, making it indispensable to precision-medicine deployment at scale.
Within this broader segment, artificial intelligence and machine learning stand out as the fastest-growing technologies, expanding at a 17.91% CAGR. AI accelerates variant interpretation, identifies mutational signatures linked to tumor aggressiveness, and optimizes algorithmic clinical-trial matching. High-throughput proteomic platforms such as SomaLogic, which quantifies 10,000 proteins from a microliter of plasma, feed dense datasets into AI models that generate early disease-risk scores and predictive biomarkers. As datasets expand, model performance improves, creating a reinforcing cycle that attracts additional R&D investment.
Together, the dominance of NGS and the scale of the broader data-analytics segment indicate a hybrid ecosystem in which sequencing and multi-omics generate the biological signal, while algorithmic platforms extract therapeutic meaning. This integration is redefining diagnostics, accelerating drug discovery, and solidifying data-centric technologies as the core enablers of next-generation precision medicine.
In 2025, hospitals and clinics accounted for 40.6% of the precision medicine end-user market, reflecting their continued role as hubs for complex genomic testing, integrated care delivery, and high-acuity decision-making. Leading cancer centers increasingly rely on molecular tumor boards, enabling oncologists, pathologists, and geneticists to match patients to targeted therapies or clinical trials within days of receiving sequencing results. Within hospital networks, rapid whole-genome sequencing is now standard in many neonatal intensive care units, where diagnostic laboratories can return actionable interpretations in under 24 hours, significantly improving outcomes for critically ill newborns.
The largest share, 59.4%, is held by the combined segment comprising diagnostic laboratories, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, contract research organizations, and other distributed testing environments. Diagnostic labs continue to scale multi-omics workflows and high-throughput sequencing, supporting everything from hereditary disease screening to liquid biopsy monitoring. Meanwhile, pharmaceutical and biotech firms are expanding investment in real-world evidence platforms, leveraging longitudinal genomic and clinical data to guide drug discovery, optimize label expansions, and support post-marketing safety surveillance.

A structural shift is underway as increasing demand moves outside traditional clinical settings. Home-care and decentralized testing environments, growing at a 16.87% CAGR, represent the fastest-expanding end-user category, enabled by miniaturized devices, digital health integration, and payer acceptance. Direct-to-consumer genetic testing kits now incorporate pharmacogenomic panels, giving patients actionable insights on medication selection without visiting a clinical laboratory. Wearable sensors stream real-time physiologic and biometric data that AI platforms integrate with genotypes to detect early disease signals. In parallel, point-of-care PCR devices deliver pathogen genotyping in under 30 minutes in community clinics, while pharmacist-run genomic counseling kiosks are being piloted in retail pharmacies to extend access to underserved populations.
Healthcare IT vendors are reinforcing this shift with secure apps that store patient genomic files, synchronize data with electronic health records, and push medication or therapy alerts directly to clinicians, improving adherence and reducing avoidable hospitalizations. As reimbursement expands for home-based testing, remote monitoring, and personalized dosing, the market is expected to migrate further away from centralized hospital labs, accelerating the decentralization of precision medicine delivery.
VII. Drivers Impact Analysis
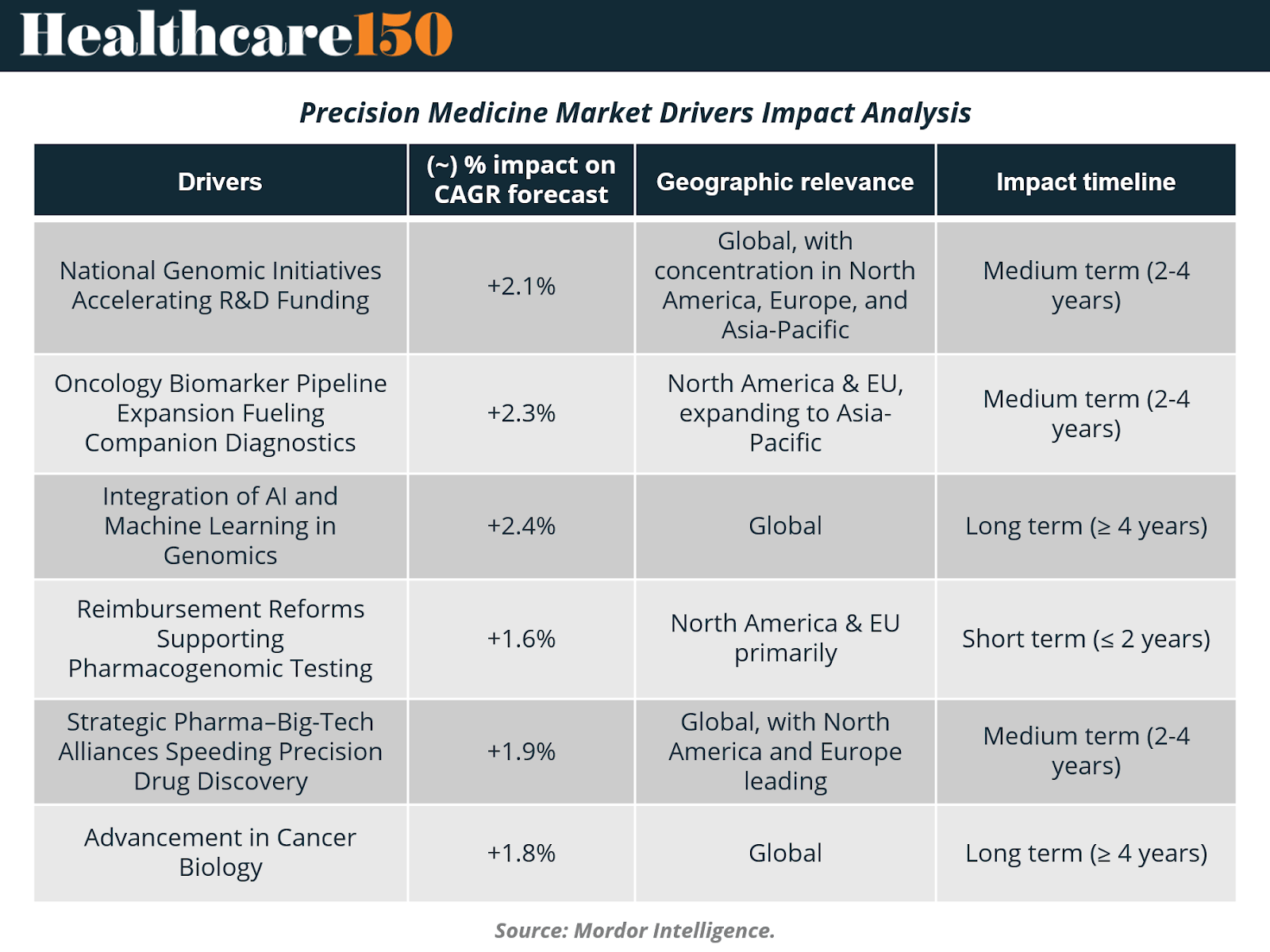
National Genomic Initiatives Accelerating R&D Funding
National genomics programs are reshaping the global research landscape by pushing sequencing and multi-omics technologies into routine clinical practice. In the United States, the NIH allocated USD 27 million to build learning health systems across six hospital networks, each designed to embed genomic workflows directly into everyday care. China’s Human Genome Project 2, targeting 80 million genomes, is set to create the world’s largest reference panel for population-scale variant interpretation. India’s release of 10,000 personal genomes in 2025 fills long-standing data gaps for South Asian populations, while Sweden’s PROMISE initiative links national patient registries with multi-omics datasets to enable real-time clinical decision support. Collectively, these efforts form interoperable, population-level data ecosystems that boost diagnostic accuracy, accelerate target discovery, and provide a foundation for large-scale precision-medicine R&D.
Oncology Biomarker Pipeline Expansion Fueling Companion Diagnostics
Precision oncology continues to be one of the most powerful structural growth drivers in the sector. Since 2024, more than 15 FDA approvals have linked targeted therapies directly to companion biomarker tests, expanding the eligible patient population for precision interventions. Illumina’s TruSight Oncology Comprehensive became the first FDA-cleared pan-cancer in-vitro diagnostic, reading more than 500 biomarkers in a single run. FoundationOne CDx now identifies NTRK fusions across tumor types to guide larotrectinib therapy, while Qiagen’s therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR Kit informs combination treatment with sotorasib and panitumumab for KRAS G12C-mutated colorectal cancer. Guardant Health’s Shield liquid biopsy adds a non-invasive colorectal cancer detection option with 83% sensitivity in average-risk adults. This rapid cadence of diagnostic approvals reinforces a co-development flywheel: more biomarkers drive more targeted drugs, which in turn expand demand for next-generation diagnostics.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Genomics
Artificial intelligence is becoming the analytical engine of precision medicine, capable of interpreting multi-layer omics datasets, proteomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, and genomics, at a scale far beyond traditional statistical tools. AI-enhanced proteomics now quantifies 10,000+ plasma proteins from a single microliter of blood, enabling ultra-early disease detection and risk stratification. Large language models increasingly function as “co-scientists,” generating hypotheses, prioritizing targets, and compressing drug discovery timelines in areas such as liver fibrosis and acute myeloid leukemia. Retrieval-augmented AI systems improve clinical-trial screening efficiency, accurately triaging candidates at a fraction of conventional costs. In clinical care, AI-enabled pharmacogenomics models predict drug–gene interactions in chronic diseases, supporting safe and personalized dosing. As every new dataset iteratively trains these models, the field enters a self-reinforcing innovation cycle, continually improving diagnostic precision and therapeutic design.
Strategic Pharma–Big-Tech Alliances Speeding Precision Drug Discovery
Collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and cloud-native data firms is accelerating the precision-drug pipeline by merging biological expertise with computational scale. GSK’s USD 1.15 billion acquisition of IDRx was fueled by strong early-phase response rates for its KIT inhibitor IDRX-42 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 23andMe now licenses its 14-million-person genomic database to Mirador Therapeutics to refine immune-disease targets, while Illumina’s USD 350 million acquisition of SomaLogic integrates high-plex 10,000-protein assays directly into its sequencing ecosystem. These alliances consolidate sequencing, proteomics, cloud computing, and AI under unified workflows, enabling faster target validation, more efficient patient identification, and tighter integration between discovery and clinical operations.
VIII. Restraints Impact Analysis

Fragmented Cross-Border Multi-Omics Data Regulations
Global precision-medicine efforts are slowed by inconsistent data-governance rules. GDPR limits genetic-data sharing across Europe, while China’s PIPL restricts outbound transfers, complicating multinational research and AI model training. These regulatory gaps prevent the formation of unified multi-omics datasets and reduce scalability for global trials.
High Cost and Limited Accessibility of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing remains expensive, particularly in emerging markets lacking reimbursement and lab infrastructure. Even in developed regions, out-of-pocket costs for multi-gene panels and pharmacogenomics can slow adoption. Limited affordability reduces eligibility for precision therapies and participation in biobanks.
Shift from Treatment-Based to Preventive Healthcare
A strategic pivot toward prevention redirects budgets away from high-cost targeted therapeutics toward lower-cost risk assessment and lifestyle programs. This transition can reduce demand for certain precision treatments, particularly in chronic disease areas.
Declining Trends in FDA Pharmacotherapy Approval Rates
Stricter regulatory standards and rising evidence requirements have slowed U.S. drug approvals. Fewer new molecular entities weaken demand for companion diagnostics and reduce biomarker-linked opportunities for drug developers. FDA trends often influence regulators globally, amplifying the impact.
IX. Conclusion
Precision medicine has moved beyond promise and into structural relevance. What began as a research-driven approach to individualized care is now reshaping clinical workflows, pharmaceutical development, and healthcare economics at scale. The market’s rapid expansion is not incidental, it reflects the convergence of sustained genomic investment, declining sequencing costs, AI-driven analytics, and increasingly biomarker-integrated treatment pathways.
At the core of this transformation lies genomic infrastructure. Rising human genome funding has enabled the data density, quality, and interoperability required to shift precision medicine from episodic use cases to system-wide deployment. Sequencing technologies continue to anchor the ecosystem, but value creation is increasingly captured by analytics platforms that translate complex multi-omics datasets into actionable clinical insight. This evolution positions precision medicine as a data-centric care model, rather than a standalone diagnostic or therapeutic category.
While adoption today remains concentrated in advanced healthcare markets, particularly the United States, the next phase of growth will be defined by geographic expansion, regulatory alignment, and decentralization of care delivery. Home-based testing, real-world evidence platforms, and AI-enabled decision support are extending precision medicine beyond tertiary hospitals, improving access while reducing system-wide inefficiencies. At the same time, persistent constraints, from fragmented data governance to affordability challenges, underscore the importance of coordinated policy and reimbursement reform.
Looking ahead, the trajectory is clear. Precision medicine will increasingly function as the operating system of modern healthcare, guiding prevention, diagnosis, treatment selection, and therapeutic development. As genomic datasets scale and analytical capabilities compound, the distinction between standard care and precision care will continue to blur. The success of the next decade will depend less on technological novelty and more on the ability of healthcare systems to integrate, govern, and act on precision insights at population scale.
Sources and References:
Fortune Business Insights — Precision Medicine Market Size & Industry Trends
Mordor Intelligence — Precision Medicine Market Analysis & Forecast
Precedence Research — Precision Medicine Market Size
Premium Perks
Since you are an Executive Subscriber, you get access to all the full length reports our research team makes every week. Interested in learning all the hard data behind the article? If so, this report is just for you.
|
Want to check the other reports? Access the Report Repository here.
